Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
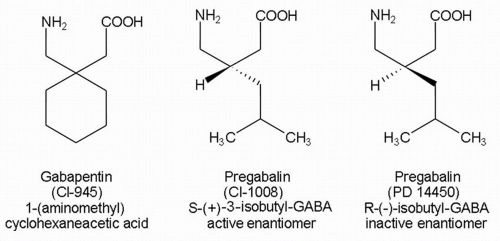
Regarding long-term safety data for the chronic use of pregabalin and gabapentin, in the case of pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, good tolerability has been observed with effective disease management (12). This review will focus on the comparative properties of gabapentin and pregabalin, specifically the available evidence on their use in the treatment of primary anxiety disorders — GAD, so-cial anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Gabapentin and pregabalin are often considered first line treatment options for various neuropathic pain conditions. The purpose of this retrospective cohort study was to compare clinically meaningful pain reduction and other relevant outcomes among patients prescribed either gabapentin or pregabali We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Tanenberg RJ, Irving GA, Risser RC, et al. Duloxetine, pregabalin, and duloxetine plus gabapentin for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain management in patients with inadequate pain response to The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain.1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety dis-orders in the United Kingdom. Gabapentin and pregabalin are considered as first-line treatment for post-SCI neuropathic pain. However, there is no study comparing the effects of gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of neuropathic pain in patients with SCI. Clinical question: Is there any evidence to support use of pregabalin as an adjuvant for neuropathic pain in a patient already on gabapentin? Review of evidence: Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin), TCAs (amitriptyline, nortriptyline) and SNRIs (duloxetine) are typical first-line treatment options for neuropathic pain. [1] Combination treatment is often needed, as less than half of Gabapentinoids, pregabalin and gabapentin were originally developed for antiseizure purposes but are now predominantly prescribed for acute or chronic pain, with approved indications limited to specific conditions. What are pregabalin and gabapentin? Pregabalin and gabapentin, collectively gabapentinoids, are primarily anticonvulsant drugs. Over the past decade, they have been increasingly prescribed for pain. 1 They are recommended for neuropathic pain in adults 2 3 (table 1), but are commonly used off-label for other pain disorders such as low back pain, sciatica, and migraine. 9 10 Pregabalin was one Manuscript Type: Original Manuscript Keywords: Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Pain Management, Adverse effects, Pharmacology Abstract: The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for Absorption and distribution Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as compared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed 2) Comparison of binding and dissociation kinetics of gabapentin, pregabalin, and mirogabalin for the α 2 δ-1 and α 2 δ-2 subunits Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, have become the drugs of choice for the treatment of neuropathic pain with positive symptoms [4]. Effect of Gabapentin versus Pregabalin on Pain Intensity in Adults with Chronic Sciatica- Prospective Observational Study. International Journal of Current Medical and Applied sciences; 2024, 43(1), 05-08. I now advocate for deprescribing gabapentin when patients do not achieve adequate pain relief for chronic neuropathic pain at a cumulative daily dose of 1800 mg. Instead, I consider pregabalin as a substitute for gabapentin in patients with inadequate pain control rather than further dose escalations. Both drugs are excreted renally, with elimination half-lives of approximately 6 hours. Pregabalin and gabapentin both show dose-response relationships in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. For neuropathic pain, a pregabalin dosage of 450 mg/day appears to reduce pain comparably to the predicted maximum effect of Lyrica, does have abuse potential. This reinforces the importance of ensuring each patient taking gabapentin has an appropriate indication, dose and frequency to maximize benefit Studies show minimal benefit & more adverse effects when high Lyrica doses are used for diabetic neuropathy (>300 mg/day) and fibromyalgia (>450 mg/day) Gabapentin and pregabalin This leaflet is about gabapentin and pregabalin, two drugs which are part of a group sometimes called gabapentinoids. The leaflet will give you some background about gabapentin and pregabalin and help you to understand how to use them in the way that’s best for you. Before taking medication for long- term pain Pregabalin vs. gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of effectiveness and safety This clinical trial aims to compare the eficacy of Pregabalin and Gabapentin in the management of this condition. Methods : A double-blind, randomized, comparative study (clinical trial registry NCT05324761 on 11th April 2022) with two parallel arms with Pregabalin and Gabapentin were used in arms one and two, respectively.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |