Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
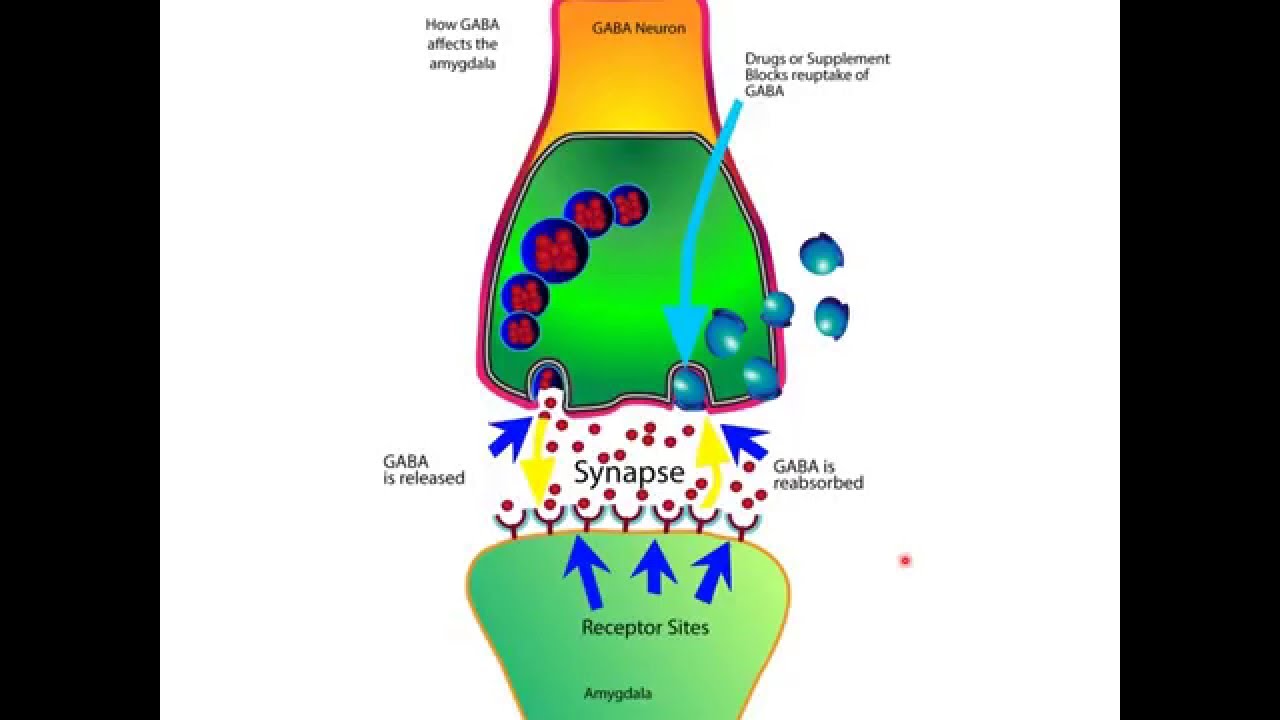
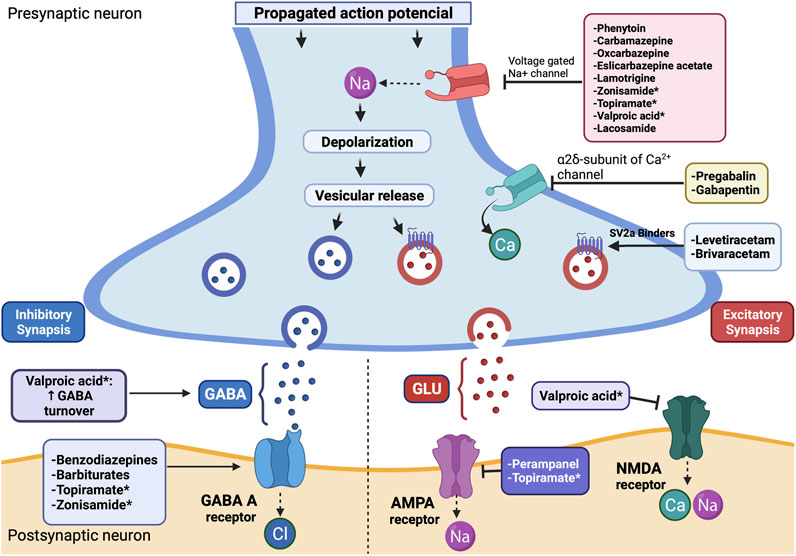
Gabapentin has no activity at GABAA or GABAB receptors of GABA uptake carriers of brain. Gabapentin interacts with a high-affinity binding site in brain membranes, which has recently been identified as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. However, the functional correlate of gabapentin binding is unclear and remains under study. Gabapentin works by changing brain electrical activity and the functioning of neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. The medication is available in pill, tablet, and liquid form. Brand names for gabapentin include Horizant, Gralise, and Neurontin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects The new work also pinpoints, for the first time, the biochemical mechanism by which the widely prescribed drug gabapentin (also marketed under the trade name Neurontin) works. "We have solved the longstanding mystery of how this blockbuster drug acts," said Ben Barres, MD, PhD, professor and chair of neurobiology. The study shows that gabapentin halts the formation of new synapses, possibly However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. How does gabapentin work in the brain? Gabapentin works by imitating the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is the brain’s major inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces neuronal excitability and activity. Specifically, gabapentin binds to a subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the brain called α2δ. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. How does Gabapentin Work ? - GabapentinGlutamate is a neurotransmitter that acts as a natural ‘nerve-exciting’ agent. It is released when electrical signals build up in nerve cells and subsequently excites more nerve cells. It is thought to play a key role in causing epileptic seizures. Reducing the release of glutamate from the nerve cells in the brain is thought to help stabilise the Gabapentin is a medication used in the treatment of various conditions such as epilepsy, post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. It works by affecting calcium channels, leading to a decrease in excitatory neurotransmitters. AI generated definition based on: Brain Research, 2016 Investigation of acute and chronic effects of gabapentin on both GABA and glutamate, particularly in brain regions typically implicated in seizure disorders, would be required to further examine gabapentin's anti-seizure effects in human subjects. Discover whether you can reverse memory loss from gabapentin and restore cognitive clarity. Explore the potential for reclaiming your memory. How does gabapentin act on the brain? Gabapentin appears to work by altering electrical activity in the brain and influencing the activity of chemicals called neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. How Does Gabapentin Work ? Gabapentin works by affecting certain neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically by modulating the action of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though its exact mechanism is not entirely understood. Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. Gabapentin is a medication that has been used for many years to help treat epilepsy, pain, and other medical conditions. It is also prescribed by some physicians as an off-label treatment for mental health disorders. Like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. This blog post will talk about what gabapentin is; how it works; its effects on the brain and body; when you should stop taking it Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such [] In this episode of I CARE FOR YOUR BRAIN with Dr. Sullivan, board certified neuropsychologist, Dr. Karen D. Sullivan provides some of the latest research on the drug, gabapentin, and its uses and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |