Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
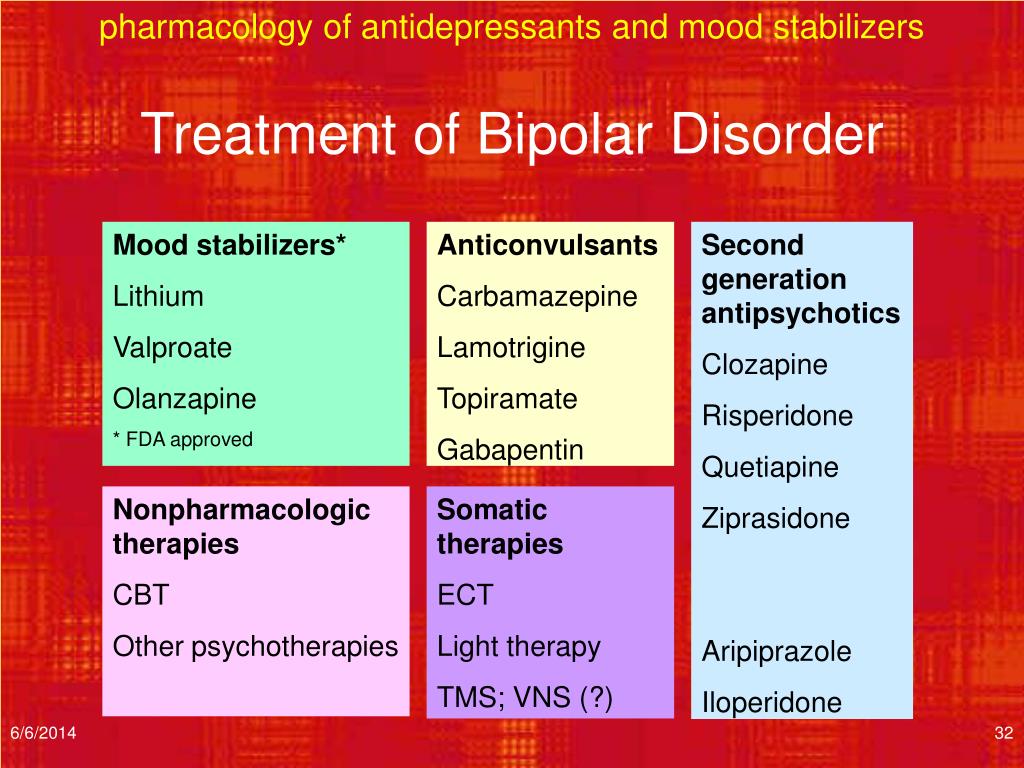
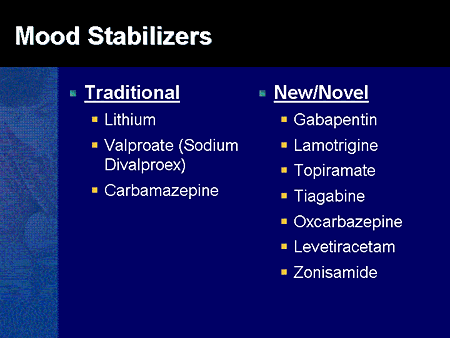
Discover how gabapentin affects emotions, from potential benefits to side effects. Learn about managing mood changes and the importance of personalized care. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Alas, a combination of antipsychotics, mood stabilizers and other classes of psychotropic medications is often the choice in this challenging patient population, despite the inconsistent and scant evidence for polypharmacy [11]. Gabapentin is a new adjunctive medication to antiseizure therapies. Anecdotal evidence suggests that it may also help to alleviate mood symptoms in patients with bipolar illness. An open-label study examined the effects of adjunctive gabapentin in bipolar patients with mixed symptoms who had previou My psychiatrist recently put me on Gabapentin for as a mood stabilizer/ to address anxiety and depression ( we're exploring a possible Bipolar II diagnosis as well). Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant. It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). Gabapentin, a new anticonvulsant with gabaergic and glutaminergic properties, has demonstrated some anxiolytic and mood-altering effects in initial clini-cal trials in patients with epilepsy.1,2 These reports are con-sistent with the possible role of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutric acid (GABA) in the pathophysiology of mood disorders,3 although gabapentin’s exact mecha-nism in Explore the intricate link between gabapentin and depression. Learn about its effects on mood disorders, mechanisms, and clinical implications.💊🧠 The relatively low frequency of bipolar disorder diagnoses in the sample of off-label gabapentin visits suggests that use of gabapentin as a mood stabilizer has declined, which corresponds with more recent psychopharmacology literature concluding that gabapentin’s mood-stabilizing effects are minimal to negligible (13, 32). Abstract Gabapentin, one of the antiepileptics, shows its effects via voltage-gated calcium channels. Sedation and mood elevation are among its side effects. The positive effects of antiepileptics such as valproate and carbamazepine as mood stabilizers have raised the hope that other antiepileptics may as well be efficacious in the treatment of mood disorders. However, relevant research data Gabapentin as an adjunct to standard mood stabilizers in out patients with mixed bipolar symptomatology. Ann Clin Psychiatry (1999) 11 (4):217–22. doi: 10.1023/a:1022361412956 Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Key takeaways: Gabapentin is a medication that’s used to treat seizures, nerve pain from shingles, and restless leg syndrome. Despite previous marketing claims, there’s no evidence that gabapentin is a good treatment for bipolar disorder. The best treatment for bipolar disorder is therapy and a combination of other medications. These include mood stabilizers, anticonvulsants, and Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. The gabapentinoids comprise gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin is licensed for use in the USA for the treatment of focal seizures and post-herpetic neuralgia [1] and in the UK for focal Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders.Â
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |