Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Management!.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
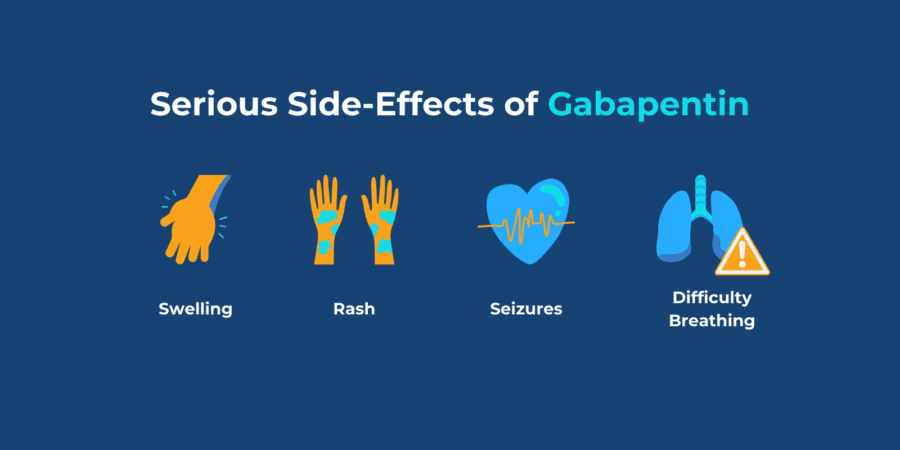 |  |
Anti-seizure medications used to treat chronic nerve pain include gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica). These medications treat the burning pain of shingles, known as postherpetic neuralgia. Overview of pharmacologic management of chronic pain in adults, including medication options and treatment strategies. Gabapentin (Neurontin) prescriptions for chronic low back pain were linked with an increased risk of dementia and cognitive impairment, especially in younger people, an analysis of U.S. healthcare Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Gabapentin, which is also used as an anti-seizure medication, has a low risk of addiction, so it's generally considered much safer than opioids for treating chronic pain. Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Neurontin is an anticonvulsant, or drug that controls seizures. Neurontin is believed to work on certain types of pain by reducing pain signals sent by damaged nerves. How do I take it? Prescribing information states that Neurontin should be taken three times a day. Neurontin comes in tablet, capsule, and liquid solution forms. Side effects Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX national database of de-identified patient records from 2004 to 2024 This topic will discuss an approach to pharmacologic management based on the type of pain and an overview of drug choices. Graded treatment recommendations can be found in treatment topics for specific chronic pain conditions (eg, chronic back pain, postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia). Therapeutics Letter 75 examines new evidence from unpublished trials on the use of gabapentin for pain. Conclusions and recommendations Misleading promotion pushed gabapentin to blockbuster status; scientific evidence suggests gabapentin has a minor role in pain control. Gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by < 1 point on a 0-10 point scale and benefits about 15% of carefully selected patients Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Gabapentin prescription in adults with chronic low back pain is associated with increased risk of dementia and cognitive impairment, particularly in non-elderly adults. Physicians should monitor cognitive outcomes in patients prescribed gabapentin. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) both belong to a class of drugs called gabapentinoids, which means they work in similar ways. They're both used to treat chronic pain in Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)--29% and 85 The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects A recent study has linked gabapentin, a popular painkiller for lower back pain, to increased risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in some adults. Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Neuropathy caused by other etiologies such as chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS), cancer, multiple sclerosis, phantom limb pain, HIV
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Management!.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |