Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
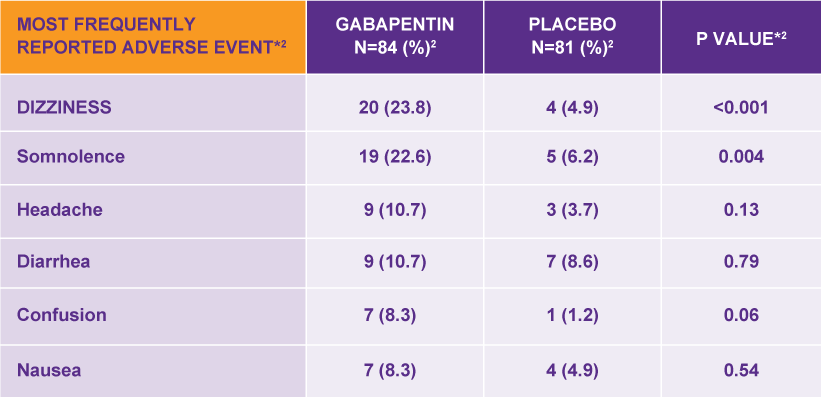
GoodRx explains in detail how Gabapentin is used to treat anxiety including dosage, side effects, and more. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric For ADHD (and depression motivation): Adderall, Adderall XR, Ritalin LA, and now Dexedrine. The issues I had with them were I'd build up a tolerance, and the side effects of some made me feel fatigued and just overall lazy. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. NEURONTIN prescription and dosage information for physicians and health care professionals. Pharmacology, adverse reactions, warnings, and NEURONTINside effects. Did you know that Gabapentin might be helpful for depression and anxiety? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that also goes by Neurontin, Gralise, or Gaborone. It’s initial purpose was to control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy, relieving nerve pain from shingles, or calming restless leg syndrome. Is gabapentin a good option for treating anxiety disorders? This is what research says and why caution is important. It has few side effects, with no known potentially fatal ef-fects, and minimal drug interactions. Patients frequently express an interest in using gabapentin rather than standard mood-stabilizing agents (like lithium carbonate, divalproex sodium, or carbamazepine) due to its limited side effect profile. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. When the decision is made to co-prescribe NEURONTIN with another CNS depressant, particularly an opioid, or to prescribe NEURONTIN to patients with underlying respiratory impairment, monitor patients for symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation, and consider initiating NEURONTIN at a low dose. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Gabapentin is a medication that is sometimes used to treat anxiety. Learn more about the uses, dosage, side effects, and potential risks of gabapentin for anxiety. Key takeaways Gabapentin is not commonly used to treat depression, but some recent studies indicate it may treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. A normal dose of gabapentin for adults can be anywhere from 100 mg to 3600 mg each day. Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, weakness, and upset stomach. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Patients 12 Years of Age and Above The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been administered in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration. Administer NEURONTIN three times a Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin, a widely prescribed medication, is primarily used to manage seizures and neuropathic pain. However, it also comes with a range of side effects, including potential implications for mental health. One of the most pressing concerns among users and healthcare providers alike is whether gabapentin can cause or exacerbate depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |