Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
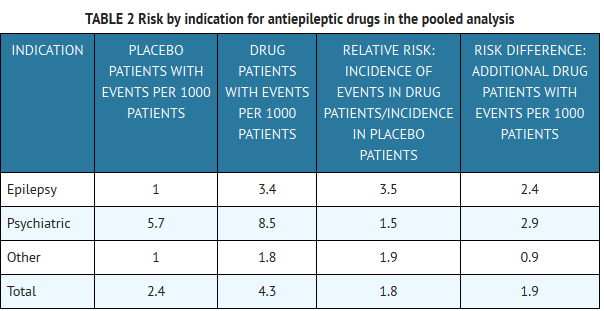
Article Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) is an anticonvulsant medication that is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS) and posttherapeutic neuralgia. GBP is commonly prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite the lack of strong evidence. However, there is growing evidence that GBP may be effective and clinically beneficial in both psychiatric disorders and substance use disorders Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. FROM THE EDITOR To keep up-to-date with the voluminous psychiatric literature, I scan many psychiatric and neuroscience publications in search of articles that pull me in for a deeper look. Recently, I skimmed the titles of a weekly email newsletter I receive and was immediately drawn to the first article: “Before You Prescribe Gabapentin, Consider These Risks.” 1 The first sentence of the While gabapentin is frequently used in practice for a wide array of psychiatric diagnoses, its use is evidence-based for only a few indications. Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. In this nationally representative sample, <1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for approved indications. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Objective: This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Objective: Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system de-pressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and While gabapentin is frequently used in practice for a wide array of psychiatric diagnoses, its use is evidence-based for only a few indications. Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. By blocking dopamine receptors, antipsychotics can help to reduce hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. While gabapentin is not approved to treat psychiatric conditions, it may sometimes be used off-label in combination with other medications to help manage certain symptoms. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has a long history of being prescribed off label for various indications, including psychiatric indications. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Neurontin Drug Usage Information Neurontin is not your traditional anxiety treatment. It was originally created as an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy though for some people who anxiety, it may be an effective treatment. Doctors that prescribe Neurontin for anxiety often only do so if the patient has been diagnosed with bipolar disorder. This use of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety is referred to as an off-label use, meaning there is limited data on its effectiveness to treat anxiety. Other off-label uses include treating alcohol withdrawal for alcohol use disorder and hot flashes associated with menopause. Systematic reviews of gabapentin treatment in psychiatric and/or substance use disorders showed inconclusive evidence for efficacy in BD, but possible efficacy for some anxiety disorders [9, 10]. Apart from its use in bipolar disorder, gabapentin has been used in patients with anxiety, panic disorder, social phobia, aggressive behavior, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). 15–21 Gabapentin has also been used in treating obsessive-compulsive disorder. 15,22,23 Other areas of clinical use have been in the treatment of substance The rise in prominence of Gabapentin coincides with our growing awareness of mental health issues and the search for versatile treatments. While its benefits for Neurontin -approved indications are clear and well-documented, the realm of mental health beckons with potential yet to be fully realized.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |