Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
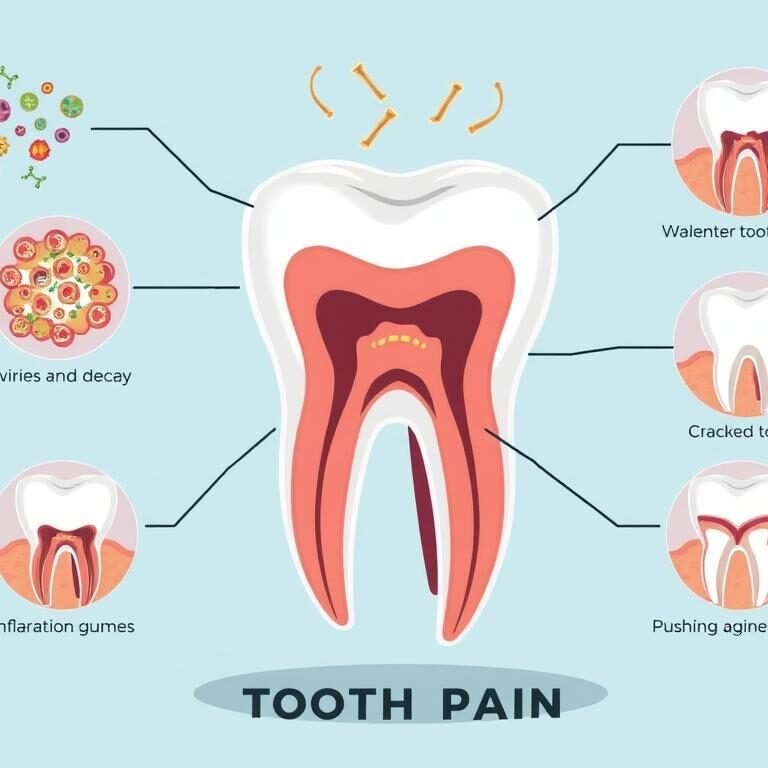
Ren and his colleagues treated over 7,000 patients at an urgent dental care clinic with different combinations of opioids, ibuprofen, acetaminophen and gabapentin after tooth extractions. The “failure rates” of the medications were determined by how often patients returned to the clinic for additional pain relief. Yes, Gabapentin can help alleviate tooth pain by reducing nerve-related discomfort. Gabapentin is typically prescribed for nerve pain, with dosages varying based on individual needs and conditions. Gabapentin has become a common medication for various types of pain, including nerve-related discomfort. Many people wonder how much gabapentin is necessary for tooth pain, especially when traditional over-the-counter medications don’t provide relief. This article explores the Gabapentin may relieve nerve pain and thus can be prescribed to treat tooth pain. Learn the potential side effects and why your dentist may prescribe gabapentin. Discover if gabapentin can help alleviate toothache pain. Learn about its effectiveness and potential benefits for toothache relief in this informative article. This cross-sectional study compares prescribing patterns of opioid and nonopioid analgesics and patients’ dental pain outcomes before vs after implementation of an opioid reduction initiative at a single dental clinic. Gabapentin may help your pain, however, gabapentin is known to cause major tooth decay. I'm living proof. I took it for 2 years for my back. Didn't do anything for my back, but it has destroyed my teeth. So far i've had to have 6 teeth pulled. They start to decay and then break off at the gum line and cannot be fixed. There is a whole section here where people are talking about the damage This article explores the potential benefits of using gabapentin to relieve wisdom tooth pain and provides insights on its usage and effectiveness. A study at the University of Rochester Medical Center's Eastman Institute for Oral Health (EIOH) found that gabapentin, when combined with ibuprofen or acetaminophen, was more effective than other pain medications in managing tooth pain. As the opioid epidemic rages on, an Eastman Institute for Oral Health study shows promise for a non-opioid alternative for acute dental pain. Gabapentin, a medication originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing nerve-related pain, including toothaches. It is effective and well-tolerated at doses of 1800 to 3600 mg/d for treating adults with neuropathic pain. These studies suggest that gabapentin can help with tooth pain, as it is effective in controlling pain and providing Customer: Can I use Gabapentin for toothache pain? Doctor's Assistant: The Dentist can help. Just a couple quick questions before I transfer you. When did the pain start? Is it localized in a particular part of your body? Customer: It’s been going on for a week and it’s in the front of my mouth. Doctor's Assistant: What type of pain is it? Is it sharp or dull, achey or stabbing? Customer Also most tooth pain is caused by nerve pain, there for gabapentin will most definitely help! Just do not take to many because you can become dizzy, loopy, and tired. Gabapentin, in combination with other analgesics, can help manage toothache pain. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant drug, has been found to be beneficial in managing dental pain, particularly when used in combination with other analgesics. Postoperative endodontic pain is an enigma for the dentist. This study aimed to evaluate the analgesic effect of 300 mg gabapentin or 75 mg pregabalin in reducing postoperative endodontic pain compared with a placebo. Ninety patients who needed root Dosage and Administration of Gabapentin for Dental Pain When prescribed gabapentin for dental pain, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines provided by your dentist or healthcare professional. Typically, the initial dosage is low and gradually increased to achieve optimal pain relief. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed schedule and not exceed the Gabapentin’s efficacy in managing various types of pain has been well-documented, but its role in alleviating tooth pain, particularly in conditions like diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia, is less clear. Over time, its applications expanded to include the management of neuropathic pain, particularly in conditions like diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. This cross-sectional study compares prescribing patterns of opioid and nonopioid analgesics and patients’ dental pain outcomes before vs after implementation of an opioid reduction initiative at a single dental clinic. A recent study from the Eastman Institute for Oral Health shows promising usage of a combination of non-opioid pain medication and adding Gabapentin as an effective method to minimize or eliminate opioids for acute dental pain. A combination of analgesics prescribed with gabapentin after dental procedures was shown to be just as effective for treating pain as opioids, researchers reported in JAMA Network Open. Qirong
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |