Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
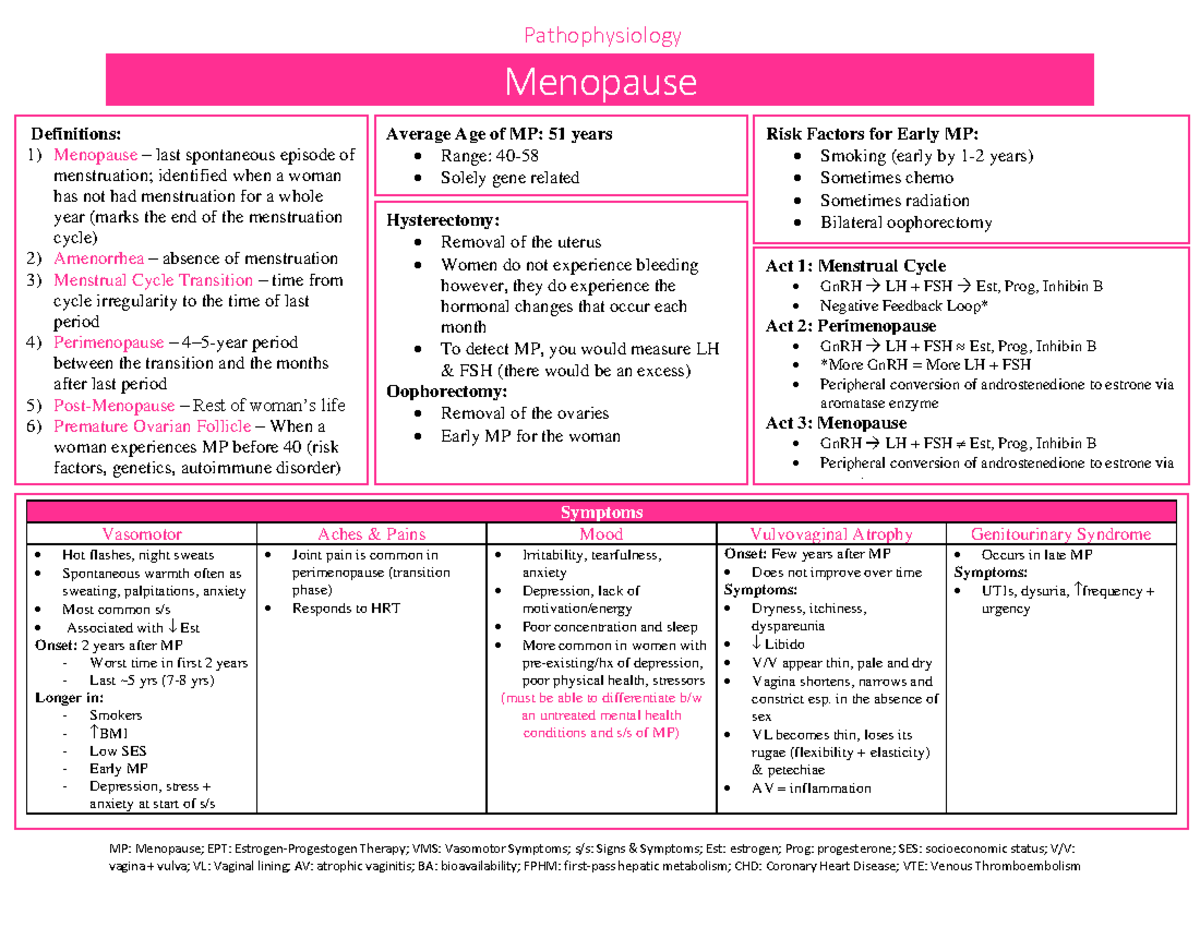
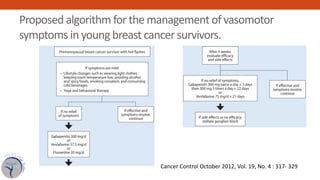
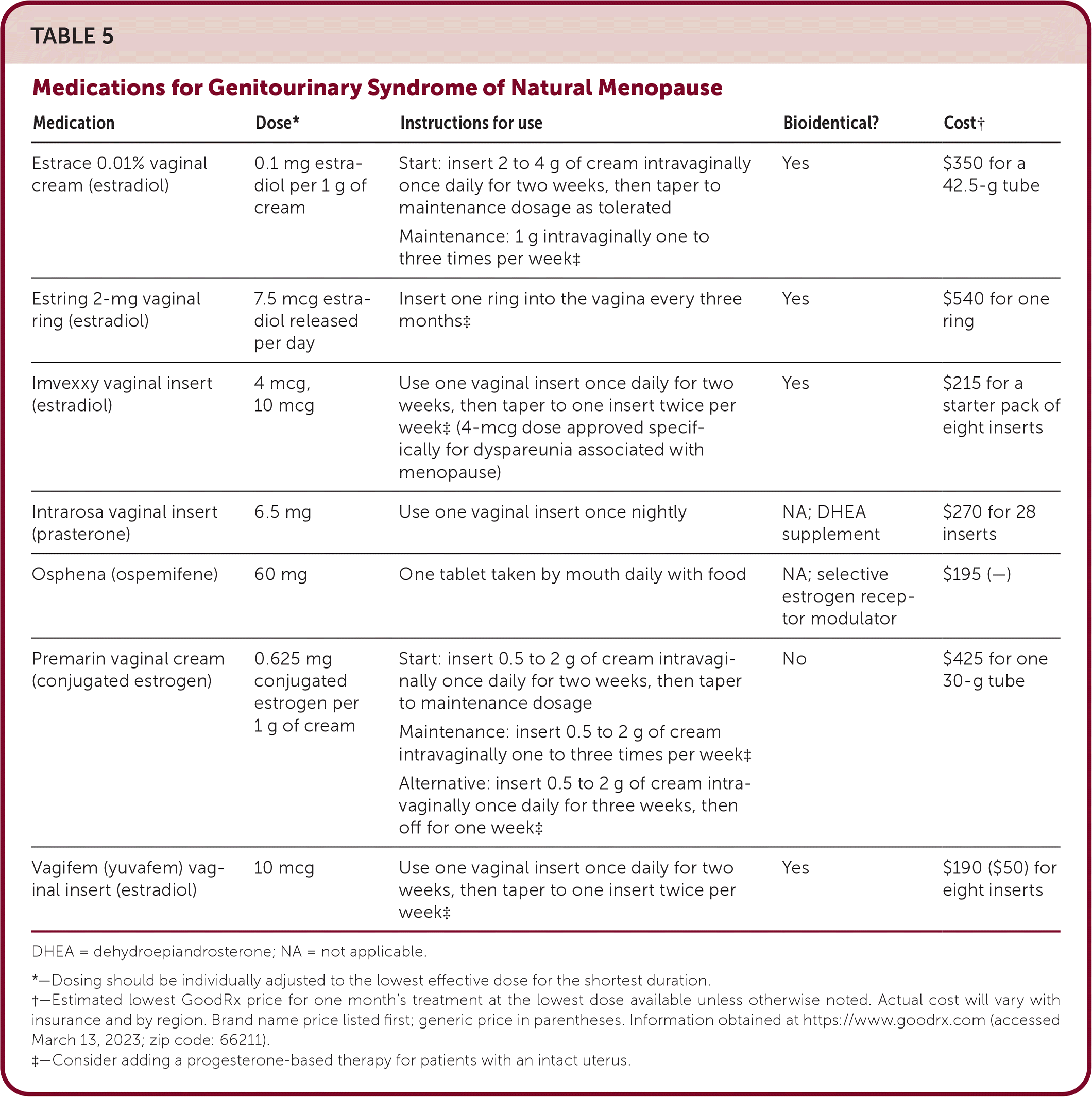
Gabapentin’s role in improving vasomotor symptoms was shown in the BREEZE 1, 2, and 3 trials, 12–18 which looked at the efficacy of gabapentin ER (Serada®; Depomed, Inc, Newark, CA, USA), an investigational drug in treating menopausal hot flashes. Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve (neuropathic) pain. It is also a non-hormonal medicine that has been shown to be effective in reducing menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin for menopausal symptoms Menopause is a normal event, but some women have troublesome symptoms such as hot flushes and night sweats. The most effective treatment is menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). Gabapentin is a non-hormonal treatment that may be prescribed for women who need, or want, to avoid MHT. Abstract Objective: To review the literature examining the use of gabapentin for treatment of hot flashes during natural or surgically induced menopause. Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. Research presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) indicates that an investigational extended release (ER) formulation of gabapentin (Serada, Depomed) is effective for the treatment of hot flashes and sleep Other medicines that might offer relief for some people include: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). This antiseizure medicine helps ease hot flashes. Side effects can include being drowsy, dizzy or tired and swelling in the arms and legs, called edema. Pregabalin (Lyrica). This is another anti-seizure medicine that can help ease hot flashes. This review investigated the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin for the treatment of hot flashes in menopausal women. Gabapentin was associated with reductions in the severity and frequency of hot flashes in menopausal women, but there was substantial variation in the results across the included trials. The authors' conclusions appear to be reliable based on the evidence presented. HRT is the current go-to treatment for menopausal hot flashes. Gabapentin offers non-hormonal relief and reduction in hot flashes and night sweats. Various non-hormonal agents have been used for the treatment of hot flashes in women with menopause. Some studies have reported that gabapentin appears to be an effective and well-tolerated treatment modality. The aim of this study was to evaluate Potential Risks and Side Effects While gabapentin shows promise in managing menopause-related sleep issues, it’s essential to consider the potential risks and side effects associated with its use. Like all medications, gabapentin can cause adverse reactions, and women considering this treatment should be aware of these possibilities. The North American Menopause society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend gabapentin as an option for managing hot flashes in women who are unwilling to take estrogen-containing supplements. earched the PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases for English-language articles published until June, 2018. The following search terms were used: “menopause,” “hot flushes,” “vasomotor symptoms,” “gabapentin,” and “non-hormonal therapy.” Primary outcomes were frequency, duration, and composite score of hot flushes. Secondary outcomes were adverse effects and Numerous reports in the medical literature and popular media have discussed the effectiveness of various nonhormonal agents in reducing menopausal hot flash symptoms. Data for these therapies are An investigational nonhormonal drug, extended-release gabapentin, effectively improved sleep and reduced hot flashes in menopausal women. Navigating menopause can be challenging, with symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances affecting daily life. While hormone replacement therapy is a common treatment, some women seek alternatives. Gabapentin, traditionally used for nerve pain, has emerged as a promising option for managing menopaus Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is used to treat vasomotor symptoms (VMS) in postmenopausal women with contraindications to hormonal therapy or who prefer alternatives. We investigated the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin for treating menopausal hot flushes via a meta-analysis. Hot flashes (HFs), defined as transient sensations of heat, sweating, flushing, anxiety, and chills lasting for 1–5 min, constitute one of the most common symptoms of menopause among women though only a few seek treatment for these. The basis of HFs Abstract Objective: To compare the effectiveness and tolerability of gabapentin with placebo for the treatment of hot flashes in women who enter menopause naturally. Gabapentin is an effective medication for managing menopausal hot flashes, offering relief by targeting neurological pathways and reducing the intensity of symptoms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |