Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
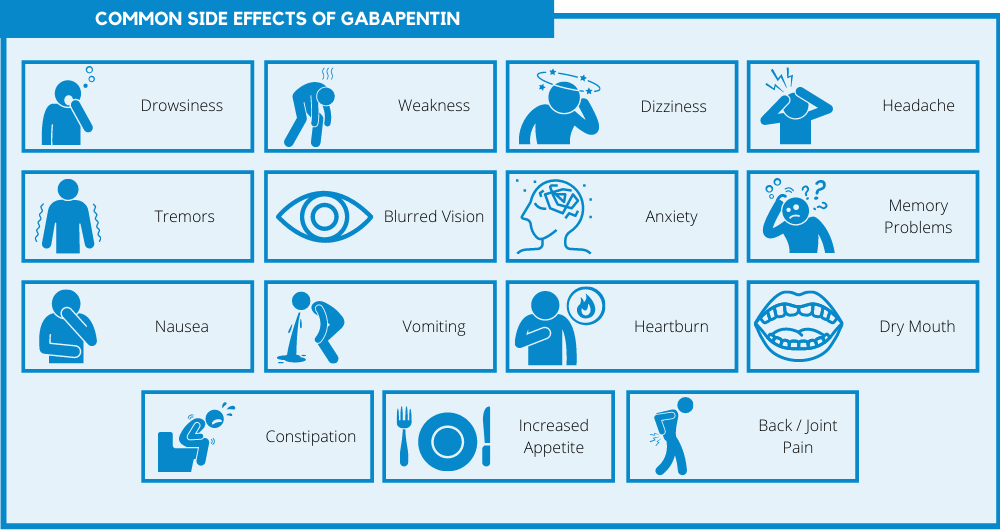 |  |
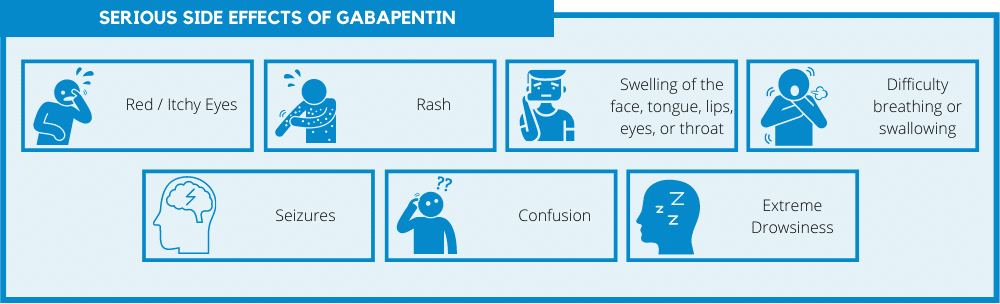
NEURONTIN (Gabapentin) Overdose - GabapentinA lethal dose of gabapentin was not identified in mice and rats receiving single oral doses as high as 8000 mg/kg. Signs of acute toxicity in animals included ataxia, labored breathing, ptosis, sedation, hypoactivity, or excitation. Acute oral overdoses of NEURONTIN up to 49 grams have been reported. In these cases, double vision, slurred speech These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. A summary table to facilitate emergency management is provided (table 1). Neurontin (gabapentin) is a medication that is used for several different conditions such as nerve pain, epilepsy, and many others. While overdoses with gabapentin are rare, it is important to know the symptoms of an overdose and the risk factors that increase the likelihood of an overdose. To avoid an overdose, take gabapentin as directed. Gabapentin (Neurontin) carries a risk for abuse, can get you high if mixed with drugs, causes adverse side effects, and can lead to overdose. Gabapentin is a medication often prescribed for anxiety, nerve pain, and seizures. However, it can be addictive and lead to overdose. Learn more here. Gabapentin is a relatively safe drug, but it should not be ingested in large amounts. Learn the possibility of gabapentin overdose and its serious withdrawal side effects. Seek Help for Gabapentin Abuse and Addiction Gabapentin is a generally safe alternative to opioids, but like all drugs, it has some risks. If you or a loved one is struggling with gabapentin abuse and at risk of an overdose or withdrawal, it’s important to seek help as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous effects. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. A summary table to facilitate emergency management is provided (table 1). The best way to avoid an overdose is to get sober and avoid abusing drugs and alcohol altogether. Here is everything you need to know about gabapentin toxicity and treatment. What is Gabapentin (Neurontin)? Gabapentin is a muscle relaxer and an anticonvulsant that is used to help control partial seizures in people struggling with epilepsy. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is most often abused in conjunction with other drugs and can cause adverse side effects. Learn about Gabapentin overdose risks. Gabapentin overdoses can be dangerous, especially when it’s used alongside other substances. Learn how to avoid a gabapentin overdose and what to do about one. Overdose can also lead to psychological effects with profound mood changes, reduced cognitive, physical, and mental abilities, and unusual behaviors. What Is Gabapentin, And What Conditions Does It Treat? Key Takeaways Gabapentin is used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain, with off-label uses for other conditions. Overdose can occur due to misuse, over-prescription, and accidental ingestion, with a growing trend of misuse among opioid users. Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose include drowsiness, muscle weakness, and respiratory depression. There is no specific antidote for gabapentin 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was Explore Gabapentin (Neurontin): comprehensive information on uses, dosage guidelines, potential side effects, and overdose risks. Learn about pill forms, pricing, and generic alternatives for this medication. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Can you overdose on Gabapentin? Understanding the risks, signs of overdose, and prevention strategies. Gabapentin, a GABA analogue, is a nonopioid prescribed for seizure control and neuralgic pain. Its abuse for recreational purposes has been increasing in recent years as the number of prescriptions also increases. In our series, we review 104 cases of decedents who tested positive for gabapentin in Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |