Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
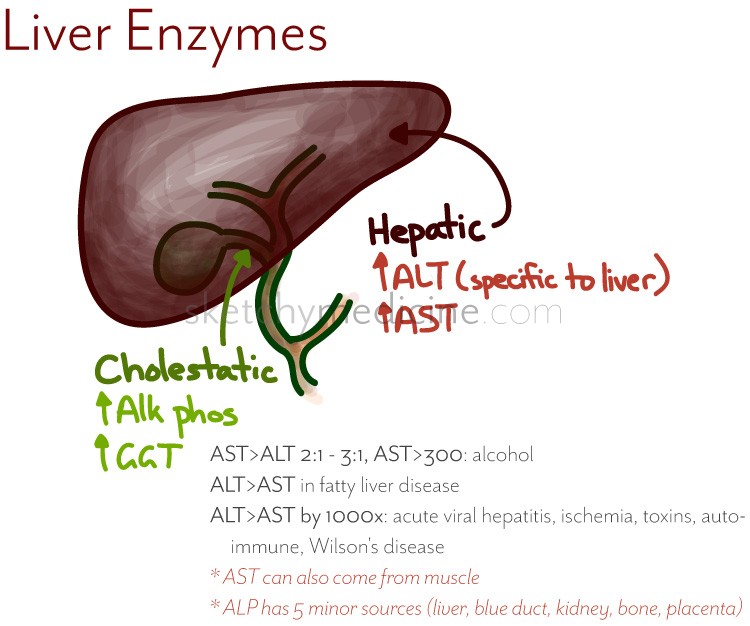
Herbal medications are not tested by the FDA. If you have liver disease, check with your doctor before taking any new medications or supplements. Liver enzymes are proteins your liver uses for normal liver functions. When your liver is damaged, these enzymes leak out into your blood and can be measured with blood testing called liver function Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Abstract- Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. Therefore this study was undertaken to find out the possibility of liver damage by this drug. Adult male (Wistar) rats of 180-220 g were administered Gabapentin is eliminated through the kidneys and, therefore, doesn’t typically cause liver injury. Learn safe dosage recommendations for people with liver disease. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is generally not harmful to the liver or kidneys, but in rare cases, it can cause DRESS syndrome. It is not metabolized by the liver and is excreted unchanged in the kidneys after circulation. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in the body. Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. However, there are a few descriptions of gabapentin-related Gabapentin is generally considered safe for the liver, but rare cases of liver damage have been reported. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained popularity for its effectiveness and relatively mild side effects. However, concerns about its impact on liver health have surfaced among patients and healthcare providers. Understanding whether gabapentin Gabapentin has infrequently been reported to cause liver injury, but the causality in previous reports is contested. Different reports suggest that gabapentin has a low profile of interaction with other drugs, hepatic enzymes, and plasma proteins. It is recommended for controlling seizures, treating nerve pain after having had shingles, and treating restless legs syndrome. Background & Aims: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are a common cause of drug induced liver injury (DILI). Over the last few decades, several newer AEDs were approved for marketing in the United States, and they are increasingly prescribed for indications other than seizures. Contemporaneous data related to trends and characteristics of liver injury due to AEDs are sparse. These findings come in consequence with some earlier studies that were carried out to determine vitamin E protective effects in different organs and different models of injury [20,56,57]. In biological systems, Vitamin E is a major antioxidant that acts as a powerful chain-breaking agent through peroxyl radicals scavenging [58] with increasing the activities of antioxidant enzymes like Introduction: Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant that is also used off-label to treat neuropathic pain. It is not metabolized by the liver, and there have been few reports of hepatotoxity associated with it. We present a rare case of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurring in a young male. Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with an extensive past medical history including type 1 Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Can gabapentin interact with other drugs that affect the liver? Yes, combining gabapentin with other medications that are known to affect the liver could theoretically increase the risk of liver-related side effects. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. High liver enzyme levels may indicate inflammation within the liver, which can be a sign of a medical condition like hepatitis or other conditions. Elevated liver enzymes might be found during routine blood testing and are usually mildly raised for a short time. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). MeSH terms Anticonvulsants / therapeutic use Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids* / adverse effects Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions* Gabapentin / adverse effects Hepatitis* Humans gamma-Aminobutyric Acid / adverse effects Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. Conclusions Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |