Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+%EF%82%90hot+flashes+45%25+vs+29%25+in+placebo.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 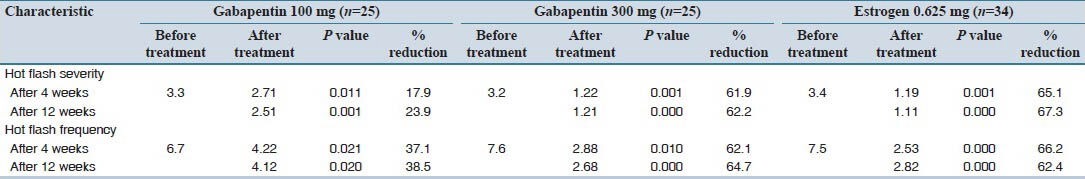 |
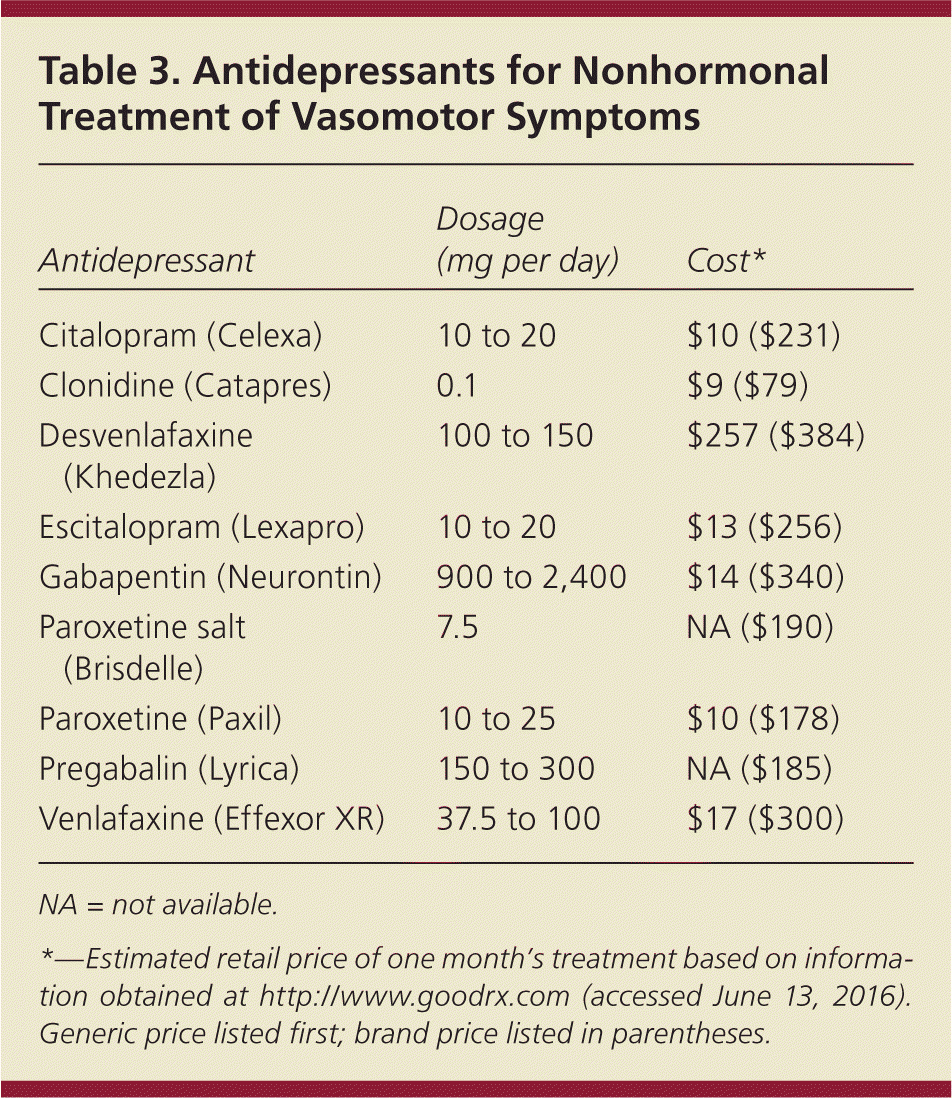
The non-hormonal medicines used to reduce hot flushes in women include gabapentin, clonidine, venlafaxine or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The treatment option depends on the individual. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® available as 100mg, 300mg, 400mg, 600mg and 800mg capsules. Also available in generic brands. Hot flashes can be a prominent problem in women with breast cancer. 1–3 In lieu of concerns regarding the use of hormonal therapies in these women, nonhormonal means of alleviating hot flashes are desirable. Older nonhormonal means of treating hot flashes (eg, a combination of belladonna alkaloids, ergotamine tartrate, and phenobarbital [Bellergal], clonidine, α-methyldopa, and vitamin E Various non-hormonal agents have been used for the treatment of hot flashes in women with menopause. Some studies have reported that gabapentin appears to be an effective and well-tolerated treatment modality. The aim of this study was to evaluate Bottom Line: Evidence supports the nonhormonal treatment of menopausal hot flashes with paroxetine, clonidine, gabapentin, and soy isoflavone extract. The overall effect size of all nonhormonal The antihypertensive agent, clonidine, was studied in the 1970s in a placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter, cross-over trial involving 100 patients with menopausal flushing. 37 This study demonstrated that clonidine significantly decreased hot flashes in a population of women without cancer. Two placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomized clinical trials were performed in women Multiple studies demonstrate modest improvement in hot flashes with clonidine. 10, 11, 23, 24, 33 One randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated a 26% decrease in hot flash frequency (P = .045 clonidine vs placebo) in patients with breast cancer. Hot flashes (HFs) are a rapid and exaggerated heat dissipation response, consisting of profuse sweating, peripheral vasodilation, and feelings of intense, internal heat. They are triggered by small elevations in core body temperature (Tc) acting Adverse effects of clonidine include dry mouth, insomnia, and drowsiness. Adverse effects of gabapentin include dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. The results revealed a classic pharmacodynamic maximal effect (Emax) model could describe the time course of hot-flash reduction by nonhormonal drugs. After deducting placebo effects, the Emax of SSRIs/SNRIs, gabapentin, clonidine, and soy isoflavones was 13.9 %, 14.8 %, 18.5 %, and 25.0 %, respectively. Clonidine, venlafaxine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, and gabapentin are nonhormonal agents that have demonstrated efficacy in small controlled and uncontrolled trials in reducing hot flashes and should be considered in patients unwilling or unable to take hormonal therapies. Clonidine and gabapentin decrease hot flash frequency The 2006 meta-analysis also included 10 RCTs (743 patients) that studied clonidine in women with and without a history of breast cancer, and 2 RCTs (479 patients) that evaluated gabapentin in women with breast cancer. 2 Both drugs reduced mean hot flash frequency (clonidine: –0.95 hot flashes/d, 95% CI, –1.44 to –0.47 at 4 weeks and Clonidine Multiple studies demonstrate modest improvement in hot flashes with clonidine. One randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated a 26% decrease in hot flash frequency (P = .045 clonidine vs placebo) in patients with breast cancer. Numerous reports in the medical literature and popular media have discussed the effectiveness of various nonhormonal agents in reducing menopausal hot flash symptoms. Data for these therapies are 2. Higher doses of gabapentin How long does it take to work? Generally hot flushes will reduce once 900mg daily dose is reached. Use of 900mg daily has been found to be effective in reducing menop usal hot flushes for at le How long is the treatment? edicine. The decision must What are the side effects? 1. Clonidine: alpha adrenergic receptor agonist/licence class anti-hypertensive and menopause symptom control Clonidine is the only non-hormonal drug with a licenced indication for control of hot flushes in the UK.21 Clonidine 25 mcg is prescribed twice daily for 2 weeks, increased up to a maximum of 50 mcg three times a day. The evidence base is contradictory, although one study shows The best way to relieve hot flashes is to take estrogen. But taking this hormone carries risks. If estrogen is right for you and you start it within 10 years of your last menstrual period or before age 60, the plusses can be greater than the risks. Medicines such as antidepressants and anti-seizure medicines also might help ease hot flashes. But they don't work as well as hormones do. Talk to ABSTRACT Although alternatives exist, hormone therapy remains the most effective treatment for menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, and it is the only treatment approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for this indication.The FDA recommends using the lowest effective dose of hormones. New low-dose preparations and new dosage forms of hormone therapy are available. What is the best nonhormonal therapy to treat hot flashes? Learn more about the new menopause treatment guidelines from a Mayo Clinic expert. While limited data demonstrate a beneficial effect of pregabalin for the treatment of hot flashes, no studies have compared its efficacy with other pharmacologic options such as HT or other nonhormonal drugs such as antidepressants, clonidine, Bellergal or gabapentin. Dosages ranged from 300 to 1,800 mg per day; however, on meta-regression analysis, gabapentin was found to have prognostic value for both frequency and severity, but not hot flush duration. 26 In one particular study, 59 postmenopausal women with more than seven hot flushes per day were randomized to either receive 900 mg/day of gabapentin
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+%EF%82%90hot+flashes+45%25+vs+29%25+in+placebo.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |