Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Parkinsons-and-alzheimers-5207704_final_rev-fcbc6a910fa841b585cde74ba3156177.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
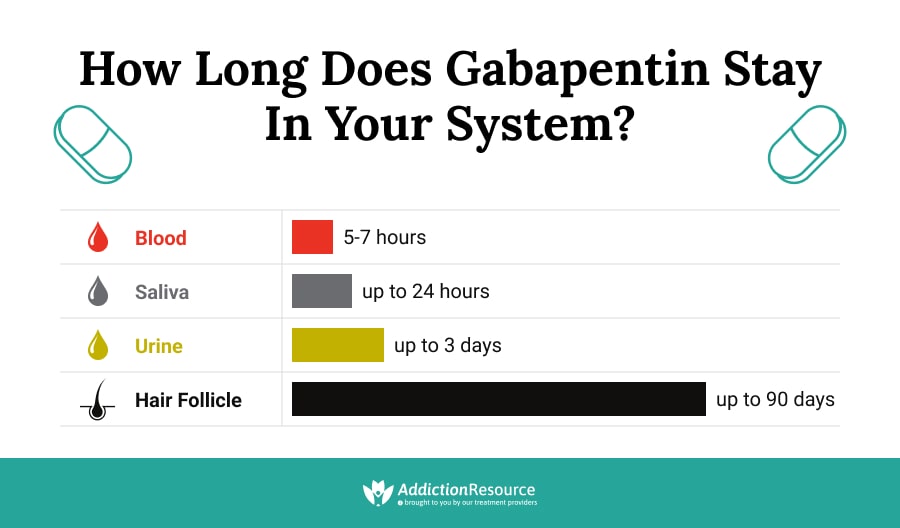 |  |
Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. Living with the cognitive changes of dementia can be challenging, and certain medications can make your symptoms worse — or may even be their cause. With the help of Gabapentin, she has stopped having seizures but does seem to be undergoing some cognitive decline that is consistent with dog dementia (circling, pacing, accidents in the house). Right now, in the morning she gets some calming bites with melatonin and CBD oil and at night some of the gabapentin. Research shows that patients with six or more prescriptions for gabapentin, commonly used to treat lower back pain, were 29% more likely to be diagnosed with dementia and 85% more likely to be diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment within 10 years of their initial pain diagnosis. Background Gabapentin has been increasingly prescribed to older adults for off-label indications, and accumulating evidence suggests potential for gabapentin misuse and related adverse events. Howev Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. What’s more, the risk was more than doubled in people normally considered too young to suffer from brain aging, those 18 to 64, results show. Adults prescribed gabapentin for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of developing dementia and cognitive impairment, particularly those under 65, according to a large-scale analysis of medical records spanning two decades. The study of over 26,000 patients found that younger adults taking gabapentin had more than double the risk of dementia compared to those not prescribed Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. I have read that long-term use of gabapentin can increase the chances of dementia. Are there specific things that I should have my regular doctor test me for because of the long-term use of Those with 12 or more gabapentin prescriptions were 40 percent more likely to develop dementia and 65 percent more likely to develop MCI, compared to those with 3 to 11 prescriptions. As we mentioned above, in most of the reviewed cases gabapentin is reported to be a well-tolerated and effective treatment for dementia-associated agitation. However, several case reports in which gabapentin was used for agitation in dementia with Lewy bodies question its appropriateness for all types of dementia-related agitation [14 – 16]. Key Takeaways: Gabapentin use has been associated with memory loss and cognitive decline. Studies suggest that the risk of dementia may be higher in patients treated with gabapentin. It is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential cognitive side effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin, which is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Especially in older adults, gabapentin is prescribed to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) (Kim et al., 2008). Several studies have reported that gabapentin has a deleterious effect on cognition (Leach et al., 1997; Meador et al., 1999; Shem et al., 2018). Gabapentin, often prescribed for chronic back pain, may raise the risk of dementia and memory issues, according to a study of over 50,000 adults. The effect was strongest in people aged 35–64 with frequent prescriptions. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin prescription in adults with chronic low back pain is associated with increased risk of dementia and cognitive impairment, particularly in non-elderly adults. Physicians should monitor cognitive outcomes in patients prescribed gabapentin. New data suggest an association between gabapentin for chronic back pain and increased risk of cognitive impairment, although experts urge caution in drawing any firm conclusions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Parkinsons-and-alzheimers-5207704_final_rev-fcbc6a910fa841b585cde74ba3156177.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |