Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
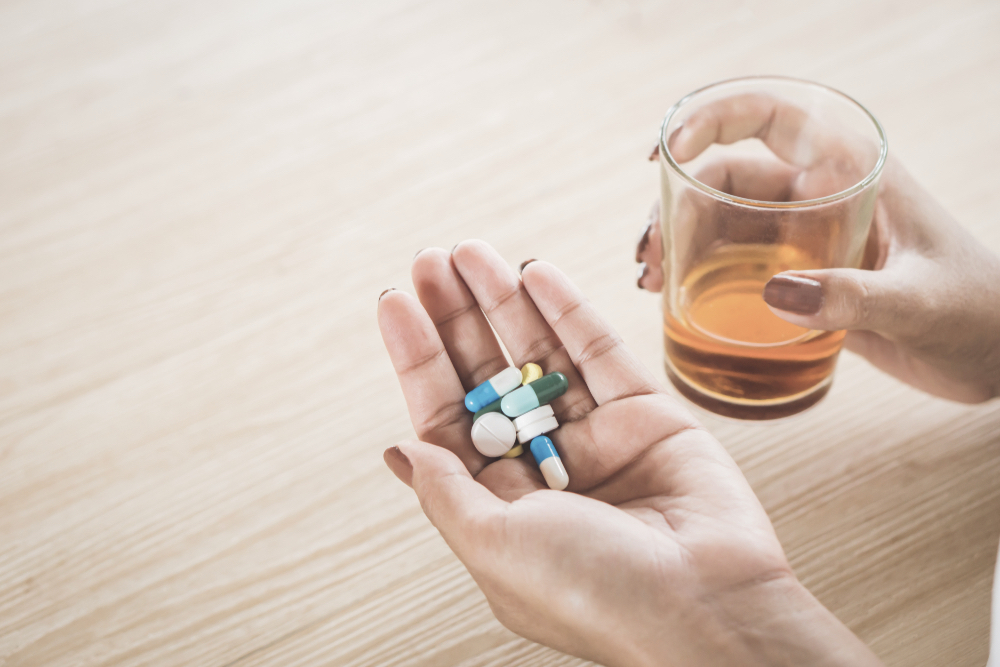 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
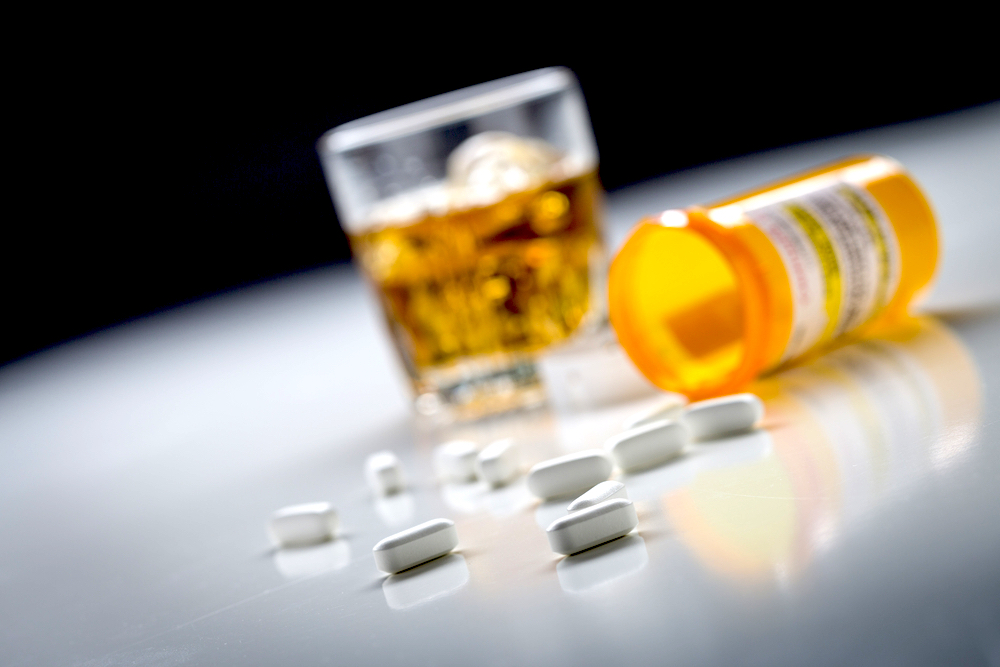
Gabapentin and alcohol co-use can lead to significant CNS impacts and increased risk of overdose. Long-term gabapentin and alcohol interaction may result in tolerance, dependence, and increased risk of accidents. Patients on gabapentin should avoid alcohol to prevent adverse effects and ensure treatment safety. Gabapentin is a prescription drug, some people use it outside its prescribed guidelines. Doing this can be dangerous, especially when combined with alcohol. Learn the serious risks of mixing gabapentin with alcohol, including cognitive impairment and impaired motor skills. Stay safe! Learn about dangerous interactions between gabapentin and alcohol. Mixing can lead to drowsiness, respiratory depression, and overdose. Know the risks and stay safe. Abstract Alcohol misuse is the fifth leading risk factor for premature death and disability worldwide. Fewer than 10% of afflicted Americans receive pharmacological treatment for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in Gabapentin and alcohol interact with the central nervous system in ways that can make their combined use highly dangerous. Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication APA’s 2018 practice guideline on AUD pharmacotherapy suggests psychiatrists consider gabapentin for patients with moderate to severe alcohol use disorder who prefer gabapentin or are intolerant to or have not responded to the FDA-approved medications naltrexone and acamprosate. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug used off-label to treat alcohol-related symptoms, but it may have risks of abuse and seizures. Learn how gabapentin works, what it can do for alcohol withdrawal and cravings, and how to prescribe it responsibly. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Gabapentin and alcohol are both depressants that can cause serious health complications when mixed. Learn about the signs of overdose, the potential for addiction, and the treatment options for substance use disorder. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence QuestionIs gabapentin efficacious in the treatment of alcohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms? FindingsIn this randomized clinical trial, gabapentin compared with placebo significantly increased the number of people with total abstinence and reduced drinking. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol produces dangerous side effects, like heavy sedation and poor coordination, multiplies overdose risks, and other health complications. Combining gabapentin and alcohol can significantly increase the risk of side effects and overdose. Learn more about the dangers of mixing gabapentin and alcohol. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol can amplify these effects, leading to increased drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, more dangerous health risks. Although gabapentin and alcohol are both legal substances, their combined use can be harmful, especially without medical supervision. This is particularly important because many medications used for alcohol treatment can have dangerous interactions if a person relapses. However, outside strictly controlled clinical environments, mixing gabapentin and alcohol could potentially increase side effects to dangerous levels. These findings were similar for other drinking variables, where gabapentin was more efficacious than placebo in the high-alcohol withdrawal group only. Gabapentin caused more dizziness, but this did not affect efficacy. Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. Expert opinion Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |