Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
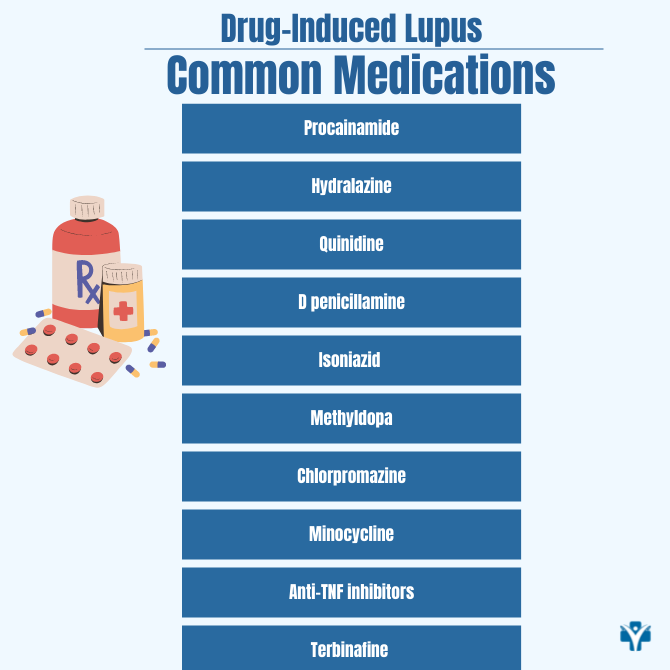
The symptoms of drug-induced lupus are similar to SLE and can include joint pain, muscle pain, fever, and sometimes a rash. However, here’s one crucial difference: drug-induced lupus rarely affects major organs, like the kidneys, brain, or heart. In contrast, SLE can impact multiple organs, often requiring more aggressive treatment. Overview Neurontin is a prescription drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat postherpetic neuralgia and some types of seizures. Neurontin is sometimes prescribed to treat neuropathic pain and seizures associated with lupus. Neurontin is also referred to by its drug name, Gabapentin. Not sure if this is a false postiive because of the Gabapentin, or if I had the lupus all along, even before the drug, or if I actually have lupus right now, and it was caused by gabapentin. Drug-induced lupus is a lupus-like disease caused by certain prescription drugs. The drugs most commonly connected with drug-induced lupus are: hydralazine (used to treat high blood pressure or hypertension) procainamide (used to treat irregular heart rhythms) quinidine (used to treat irregular heart rhythms) Drug-induced lupus is more common in men because they are given these drugs more It can be hard for doctors to diagnose drug-induced lupus since symptoms typically begin long after you start the medicine. Your doctor may ask you about your medical history and do a physical exam. The list of medications associated with drug-induced lupus is growing, highlighting the need for awareness and careful monitoring in clinical practice. At least 46 drugs currently in use can cause drug-induced lupus. While lupus-inducing drugs are typically those used to treat chronic diseases, no obvious common denominator links the drugs. That said, the clinical features and laboratory abnormalities in lupus induced by most drugs are remarkably What does gabapentin do for lupus Related Questions Can drug-induced lupus be cured? There’s no specific treatment for drug-induced lupus other than to stop taking the medication. You should begin to improve within a few weeks, though it can take longer for symptoms to go away completely. Generally, no other treatment is needed. Several very different aspects need to be considered. Some drugs are potential inducers of lupus. In genetically predisposed people, their prolonged intake can trigger induced lupus, which most often heals after stopping the drug. It would therefore seem logical to ban these drugs in patients with "spontaneous" lupus (of unknown cause), for fear of making the disease worse even if such a risk Drug-induced lupus has been reported as a side-effect of long-term therapy with over 40 medications. Its clinical and laboratory features are similar to systemic lupus erythematosus, except that patients fully recover after the offending medication is discontinued. Drug-induced lupus is an autoimmune disease that occurs after taking certain medications. Symptoms include joint pain, fever, and fatigue. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus (DILE) is a lupus-like autoimmune disorder, which usually occurs with chronic exposure to certain drugs (months to years) and resolves after cessation of the culprit medication. US Pharm. 2011;37 (1):HS6-HS8. Drug-induced lupus (DIL) is one of the most widely described drug-induced rheumatologic syndromes. 1,2 It has been estimated that up to 10% of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) cases are drug induced, which approximates to 15,000 to 30,000 cases per year. 3,4 Sulfadiazine was the first drug to be implicated in the causation of lupus in 1945. 5 A definite Learn about drug-induced lupus, a rare adverse reaction to medications that mimics the symptoms of the autoimmune disease. Drug-induced lupus (DIL) is a condition where certain medications may trigger symptoms that resemble those of lupus, an autoimmune disease. Unlike systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), DIL may be triggered by specific medications and typically improves once the medication is discontinued. Treatment of drug-induced lupus If possible, the medication suspected of causing drug-induced lupus should be discontinued or replaced with a similar drug. In most people who develop drug-induced lupus, after the causative medication is discontinued, the ANA should gradually disappear. Its decline can confirm the diagnosis. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder that is triggered by a reaction to a medicine. Drug-induced lupus (DIL) is an autoimmune phenomenon where a drug exposure leads to the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) like clinical features. DIL is a clear example of an environmental trigger leading to the development of lupus in a genetically susceptible individual. Hydralazine was the first agent to be associated with the development of lupus-like symptoms in 1954[1 Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve pain caused by lupus, though it comes with potential risks that should be understood. About 21 percent of people with lupus develop nervous system complications within the first seven years, which can affect the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system, causing various symptoms including pain, numbness, and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |