Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
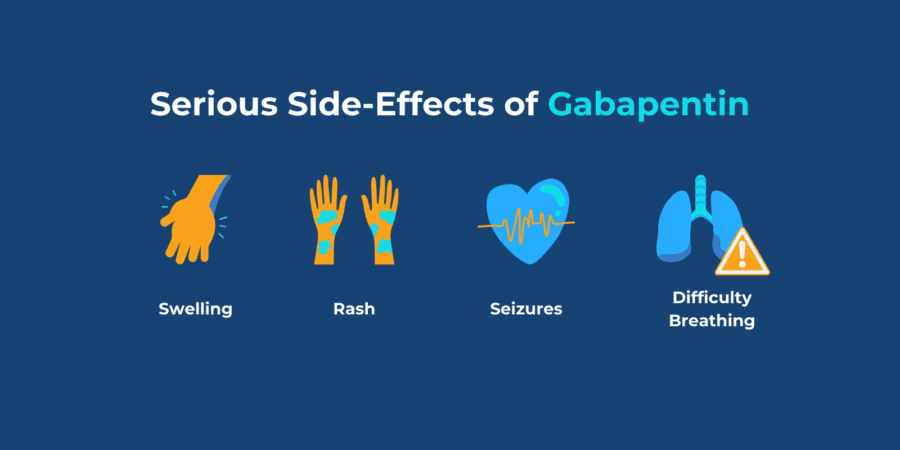
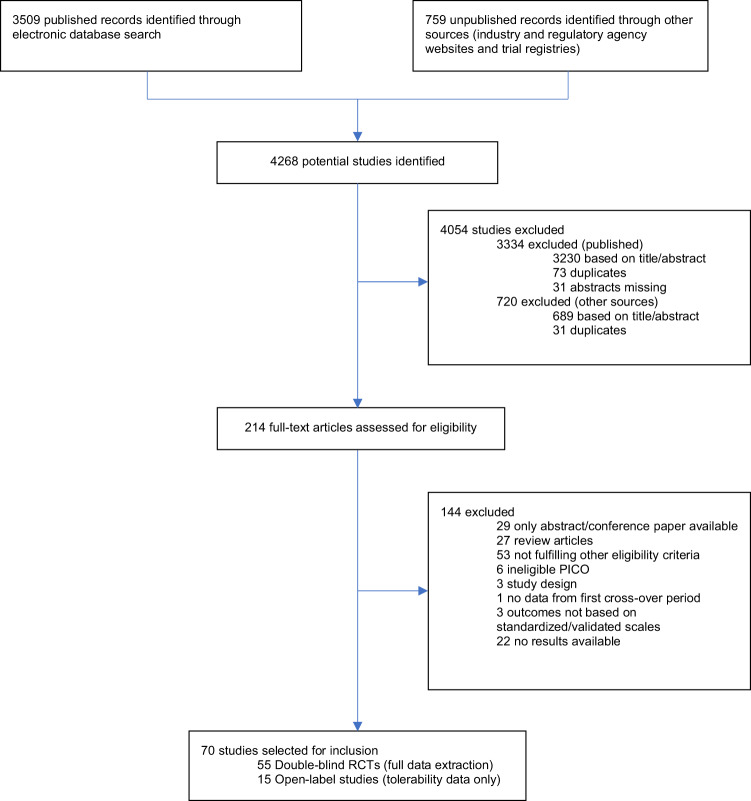
Gabapentin and pregabalin in bipolar disorder, anxiety states, and insomnia: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and rationale Key takeaways: Gabapentin is a medication that’s used to treat seizures, nerve pain from shingles, and restless leg syndrome. Despite previous marketing claims, there’s no evidence that gabapentin is a good treatment for bipolar disorder. The best treatment for bipolar disorder is therapy and a combination of other medications. These include mood stabilizers, anticonvulsants, and As for Neurontin itself, the results are fairly mixed. It is used for such a specific purpose (reducing anxiety in bipolar patients) that it can be hard to differentiate between the anxiety reduction qualities of other medication concurrently prescribed to treat bipolar and the anxiety reduction qualities of Neurontin. Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. I take gabapentin for anxiety and it barely helps me. I take 900mg/day but apparently the highest dose is in the thousands. I just started depakote so I don't wanna increase gabapentin until my mood stabilizes. Gabapentin is pharmacodynamically close or identical to pregabalin, and is available at low cost in the United States. Gabapentin could theoretically represent a reasonable alternative to pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, but available evidence does not fully support this hypothesis. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about gabapentin for anxiety. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription drug or medication that is FDA-approved to treat nerve pain and seizure disorders. It also has other uses—including treating anxiety disorders—though it has not been FDA-approved to be used for this purpose. The drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are sometimes prescribed for people with bipolar disorder or insomnia. Research found little evidence that they are effective. The drugs have side effects and can be addictive; the team calls for further trials. Gabapentin and pregabalin (collectively known as gabapentinoids) are licensed in the UK to treat pain and seizures. Gabapentin for Anxiety, Depression, and Bipolar Disorder The prescription drug is being used off-label to treat common mental illnesses and even alcohol use disorder. Systematic reviews of gabapentin treatment in psychiatric and/or substance use disorders showed inconclusive evidence for efficacy in BD, but possible efficacy for some anxiety disorders [9, 10]. Abstract Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent comorbid diagnoses in patients with bipolar disorder (BD). A comorbid anxiety diagnosis can significantly impact the severity of bipolar symptoms, increase the risk of suicidality, and decrease psychosocial functioning and quality of life. In conclusion, gabapentin’s journey from an anticonvulsant to a tool in mental health treatment is a testament to the complex and interconnected nature of our brains. While it’s not a panacea, it offers hope and potential relief for many individuals battling anxiety, mood disorders, and other mental health challenges. Abstract Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Gabapentin and pregabalin have often been prescribed off-label in spite of This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric Gabapentin appears to have some benefit for anxiety disorders but failed to show benefit in bipolar disorder trials. In the individual patient with a mixed psychiatric disorder, benefits are most likely due to anxiolytic effects. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α<sub>2</sub>δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric indications, and there is increasing concern abou Evidence also suggests gabapentin is more effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and certain types of anxiety than conditions like bipolar disorder, panic disorder, or panic attacks. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |