Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
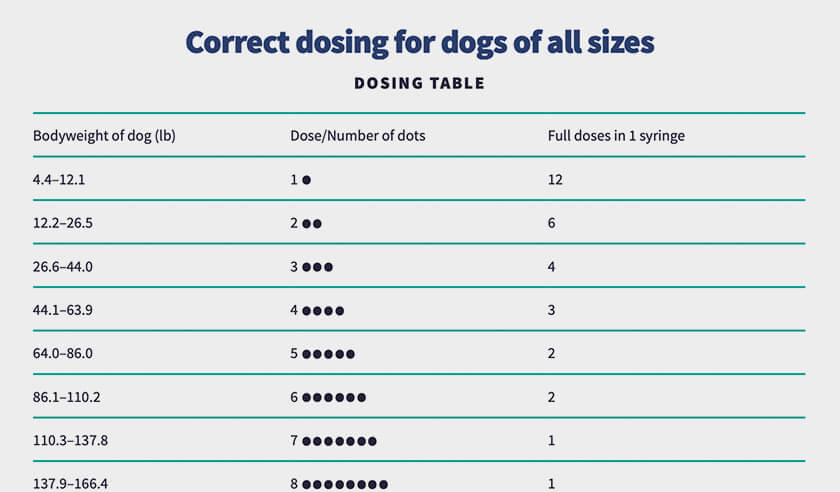 |  |
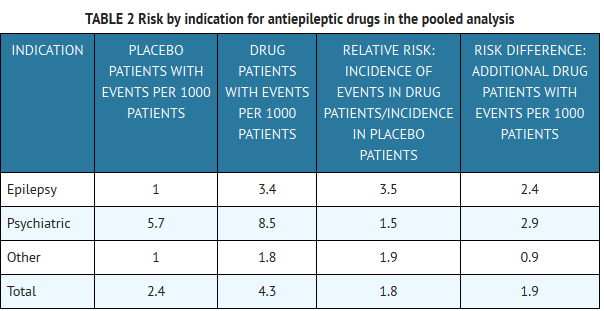
In adult patients, the half-life of gabapentin is about 5 to 7 hours. In other words, it takes the body about 5 to 7 hours to eliminate its gabapentin concentration by half. In dogs, gabapentin has a relatively short half-life, which is the time it takes for the concentration of the medication to reduce by half. The half-life of gabapentin in dogs is approximately 3-4 hours, although this can vary depending on the individual dog and the dosage administered. Gabapentin has a short half-life in dogs —typically 3 to 4 hours—which means that missing a dose may allow symptoms (pain, anxiety, seizures) to re-emerge fairly quickly, depending on the indication. If your dog suffers from chronic pain or seizures, chances are you have heard about Gabapentin. But what is Gabapentin? Is it safe for dogs? And how is it used? In this article, we will answer these questions and talk about Gabapentin for dogs. In veterinary medicine, Gabapentin is used "off-label" and in conjunction with It should be mentioned that gabapentin has extremely short half-life and consequently stays within the dog’s system for no more than 2 to 3 hours. Last but not least, although gabapentin for humans is same as gabapentin for dogs, the human dosage is totally different from the canine dosage. In dogs, however, a remarkable formation of N-methyl-gabapentin is found. Elimination half-lives range between 2-3 h in rats, 3-4 h in dogs, and 5-6 h in man. Gabapentin is nearly exclusively eliminated via the kidneys. Renal elimination was up to 99.8% in rats and approx. 80% in man following oral administration. Gabapentin has a half-life of around 5-7 hours in dogs, meaning it will be eliminated from their system within a day or two. However, the effects of the medication may last longer due to its cumulative nature in the body. This review aimed to clarify gabapentin use and pharmacokinetic aspects to promote conscious use in dogs, cats, and horses. In dogs, gabapentin was beneficial in the treatment of epilepsy, as well as chronic, neuropathic, and post-operative pain, as well as anxiety. It has a short half-life (3.3 to 3.4 hours in a study of the pharmacokinetics of oral gabapentin in Greyhound dogs). This means the body has broken down and eliminated half of the dose in about 3.5 hours. However, the exact duration for Gabapentin to be eliminated from a dog’s system can vary. Factors such as the dog’s age, weight, metabolism, and overall health can influence the clearance time. Typically, Gabapentin has a half-life of around 3 to 4 hours in dogs, meaning it takes roughly that amount of time for half the drug to be eliminated. However, the exact duration for Gabapentin to be eliminated from a dog’s system can vary. Factors such as the dog’s age, weight, metabolism, and overall health can influence the clearance time. Typically, Gabapentin has a half-life of around 3 to 4 hours in dogs, meaning it takes roughly that amount of time for half the drug to be eliminated. Gabapentin has a very short elimination half-life in dogs and cats after oral and intravenous administration (three to four hours). Therefore, it needs to be administered (at least) every eight hours 6, 9. The purpose of this study was to assess the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in healthy greyhound dogs after single oral doses targeted at 10 and 20 mg/kg PO. Six healthy greyhounds were enrolled (3 males, 3 females). Blood was obtained at predetermined times for the measurement of gabapentin plasma concentrations by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic parameters were This review aimed to clarify gabapentin use and pharmacokinetic aspects to promote conscious use in dogs, cats, and horses. In dogs, gabapentin was useful in the treatment of epilepsy, as well as chronic, neuropathic, and post-operative pain and anxiety. The half-life is the amount of time it takes for the blood levels of a specific drug to decrease by half. The half-life of gabapentin in dogs is 2 to 3 hours, the same as it is in humans and rats. This means that although gabapentin doesn’t linger around for very long, regular dosing enables it to have a cumulative effect. Distribution In dogs and cats, it takes approximately 2 weeks to reach a steady-state plasma concentration of phenobarbital because of the drug's long half-life (in dogs, 37–75 hours [mean 53 hours]; in cats, 35–56 hours [mean 43 hours]). Phenobarbital is highly protein bound. Understanding gabapentin half-life in dogs is crucial for effective pain management and seizure control. The elimination of gabapentin from a canine's system is a complex process influenced by various factors, including the dog's age, breed, metabolism, and the specific dosage administered. This variation necessitates careful monitoring and potential adjustments to the prescribed regimen Maximum blood levels are achieved in one to three hours and it has an elimination half-life of three to four hours.6 Gabapentin is excreted almost completely by the kidneys and it does not rely on hepatic biotransformation,7 making it a good choice for patients with hepatic disease. In general, however, gabapentin has a relatively short half-life in dogs, meaning that it is eliminated from the body relatively quickly. Studies have shown that gabapentin has a half-life of around 3-4 hours in dogs, which means that it can take anywhere from 12 to 24 hours for the drug to be completely eliminated from the animal’s system.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |