Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | -manufacturing-plant.webp) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
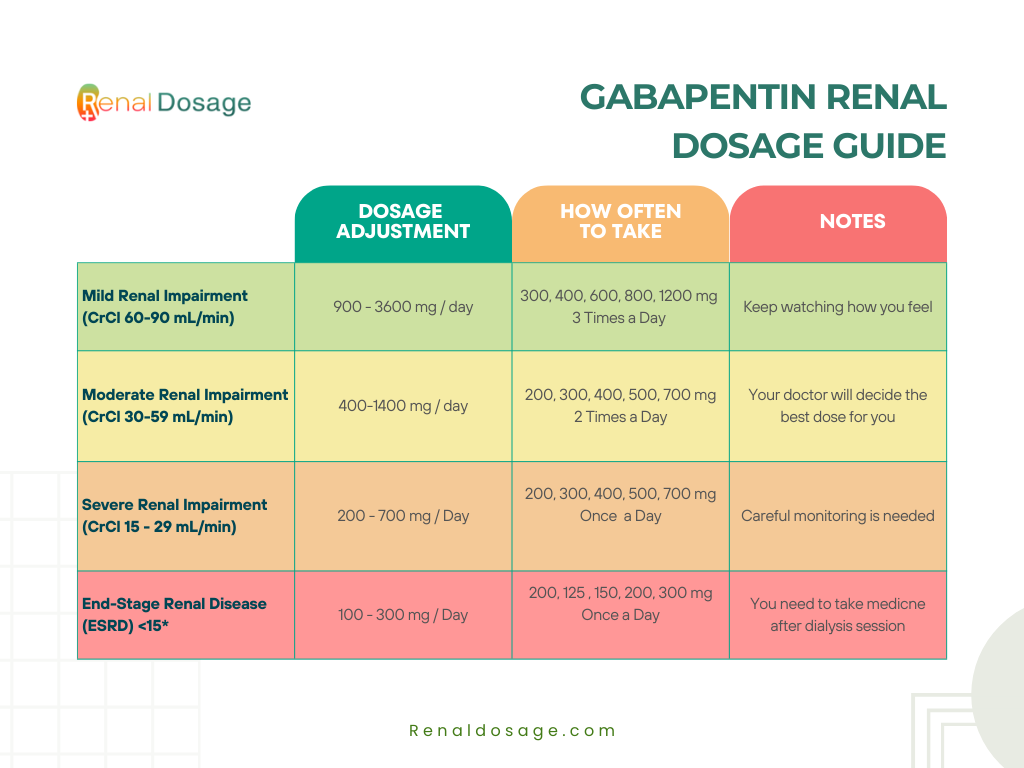
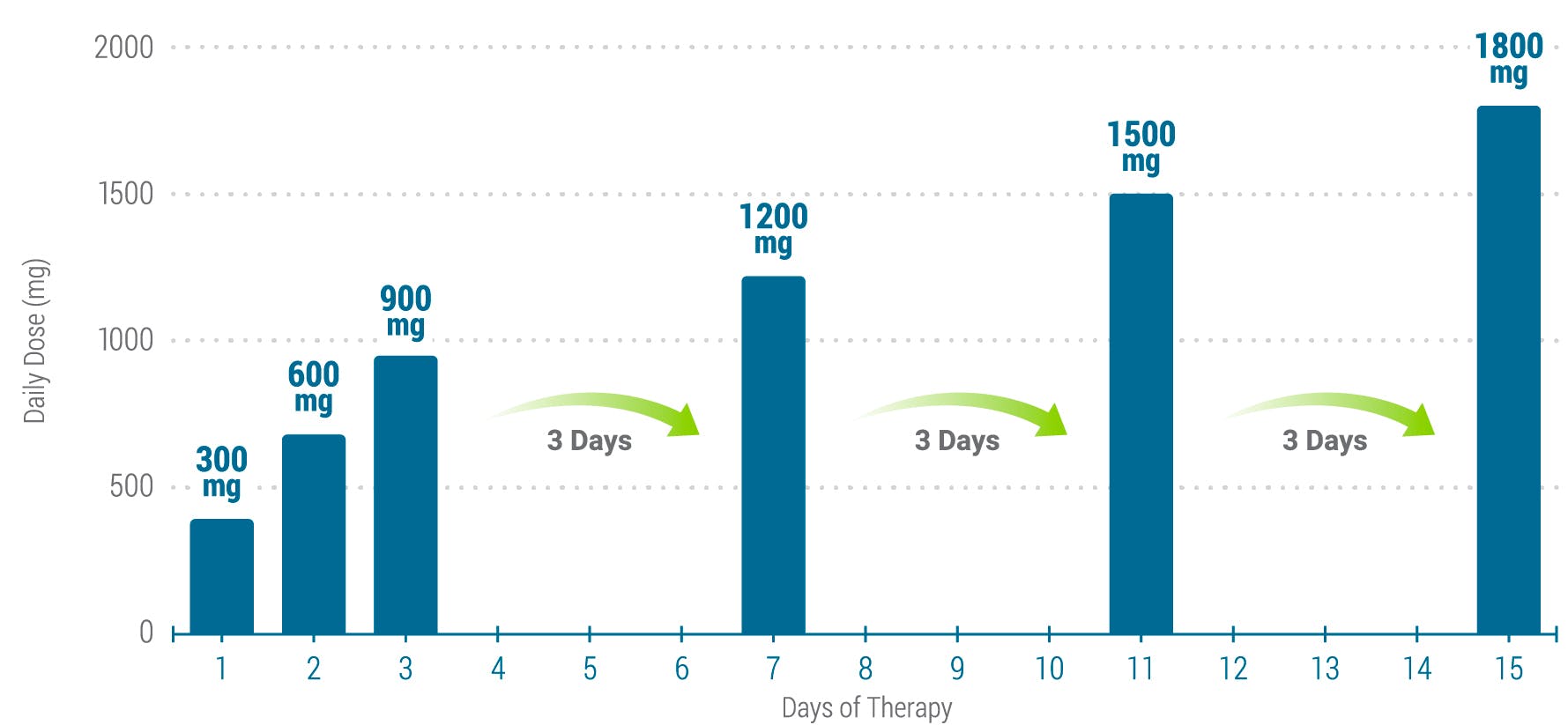
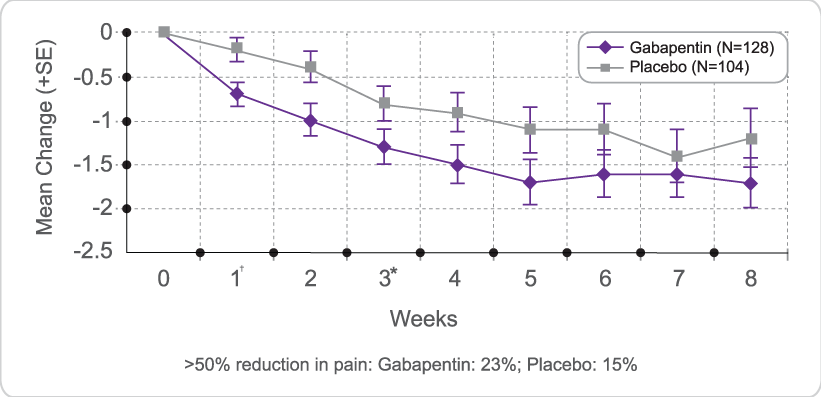
Slower titration of gabapentin dosage may be appropriate for individual patients. The minimum time to reach a dose of 1800 mg/day is one week, to reach 2400 mg/day is a total of two weeks, and to reach 3600 mg/day is a total of three weeks. Slower titration of gabapentin may be appropriate for individual patients to improve tolerability. Once a patient is on a 900mg dose, the dose can be increased in 300mg increments every two to three days until tolerated. The dose should be increased to either the dose that provides sufficient pain relief or the maximum tolerated dose. Note 4- Gabapentin has been associated with a rare risk of severe respiratory depression even without concomitant opioid medicines. Patients with compromised respiratory function, respiratory or neurological disease, renal impairment, concomitant use of CNS depressants, and elderly people might be at higher risk of experiencing severe If on amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin or pregabalin as initial treatment for neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) and is not effective or is not tolerated: Offer one of the other three remaining drug options (for example if on amitriptyline, switch to duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin). Initiate dose at 10mg/night and gradually up-titrate as tolerated at 2-4 • Counsel patient that it can take up to 12 weeks to achieve a therapeutic week intervals up to 25mg/night to allow acclimatisation of potential side- response. Suggested fast up-titration for Gabapentin: Consider slower increase in dose of gabapentin when patient presents symptoms of milder pain, they are elderly or have renal impairment. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It also has some effect on spasticity and can be used in combination with other drugs as an off-label use; it is particularly useful if pain and spasticity co-exist. The maximum dose is 3600 mg per day in divided doses. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Therapeutic dosing targets Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). CKS recommends using clinical judgement to decide how soon to follow up a person with neuropathic pain because the urgency of a follow up will depend on several factors, including the cause of neuropathic pain, severity of pain, treatment prescribed, and the complexity of the titration process. Gabapentin 100 mg hard capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) by Morningside Healthcare Ltd Pregabalin and gabapentin are both options, as are low dose dopamine agonists. Dopamine agonists can cause augmentation (drug induced worsening) of symptoms in some patients and are therefore sometimes a cause for escalating symptoms. Dopamine agonists may be a preferred choice in the obese or in those with type II diabetes. Ensure that the risk of side effects is reviewed for patients in this cohort co-prescribed a strong opioid. Ensure that dosing of gabapentinoids in this patient cohort is as safe as possible in relation to renal function. Reduce the risk of patients experiencing avoidable harm from gabapentinoids when used for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin DOWN-TITRATION / WITHDRAWAL Total daily dose ≤900 mg: Reduce total daily dose by 100 mg every 4 days. Total daily dose >900 mg: Reduce total daily dose by 300 mg every 4 days unless observations of emergent symptoms are required, in which case more gradual dose tapering is needed, as seen in table below: Gabapentin, Prescribing information, Restless legs syndrome, CKSThe use of gabapentin for restless legs syndrome (RLS) is off-label. Initial dose of 300 mg if the person is under 65 years old and 100 mg if the person is over 65 years old. Maximum recommended dose for RLS is 2700 mg. CKS did not identify any specific guidance on dose titration for use in RLS. However, for other indications it NICE guidance suggests for all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin or pregabalin should be offered as initial treatment for neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) (1) from previous guidance there is some advice about titration for amitriptyline Co-prescribing of opioids and gabapentinoids should be avoided if possible, due to the increased risk of respiratory depression, accidental overdose, and death. The MHRA and manufacturers advise that when prescribing gabapentin in patients who require concomitant treatment with opioid medicines, patients should be carefully observed for signs of CNS depression, such as somnolence, sedation A titrated approach for initiation of both gabapentin and pregabalin is recommended, Titration of doses should be managed according to side effects and clinical effectiveness. taking into consideration patient characteristics, e.g. elderly, renal impairment, breast feeding which may affect the suitability for prescribing or the dosage. Dose titration for gabapentin. Dose titration for pregabalin. onse and tol
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | -manufacturing-plant.webp) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |