Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
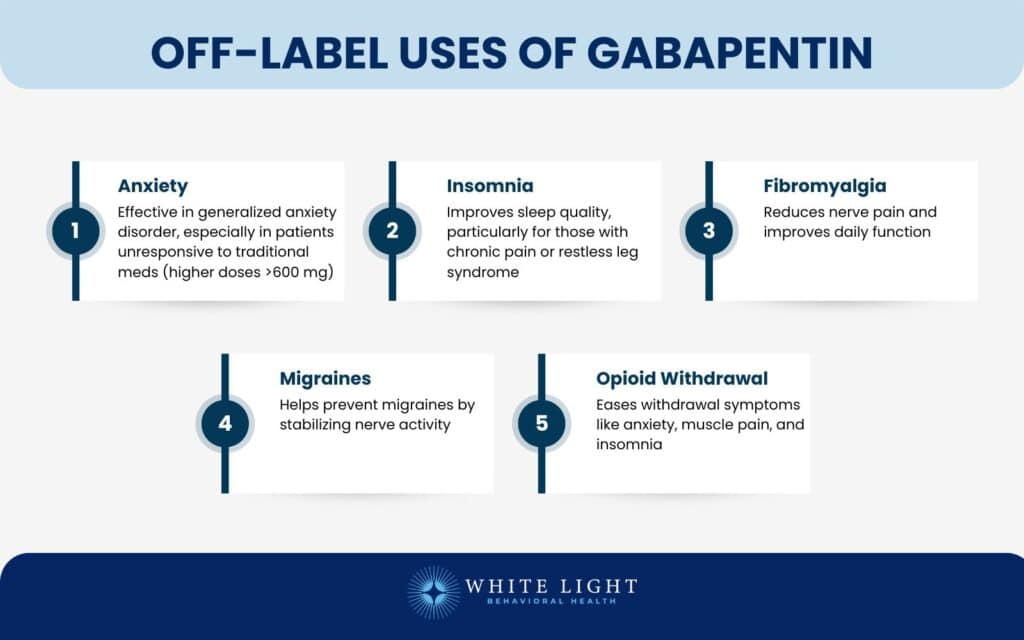
Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Abstract Objective: The objective of the study was to explore the experiences of physicians prescribing gabapentin off label. Methods: We used a case study approach to explore the experiences of physicians prescribing gabapentin for off-label indications. Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 10 physicians (psychiatry, pain and neurology specialists) in the Greater Toronto Area. Data Various off-label (unapproved) uses have been reported, and the use of gabapentin for off-label purposes has reportedly exceeded use for FDA-approved indications. Pharmaceutical marketing practices and physician dissat-isfaction with currently available pharmacological treatment options may be key factors that contribute to this prescribing trend. Use of gabapentin has increased since 2008; use of pregabalin has remained steady. Between 2017 and 2021, most patients using gabapentinoids reported having musculoskeletal pain and diabetes. Despite limited indications, gabapentin and its cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica), are widely prescribed off-label for various other pain syndromes. This Special Communication summarizes the limited published evidence to support off-label gabapentinoid uses, describes clinical cases in which off-label use is problematic, and notes how review articles and guidelines tend to overstate gabapentinoid effectiveness. Off-Label Usages of Gabapentin - Gabapentin - GabapentinGabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for a variety of conditions outside its primary approvals for epilepsy and nerve pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is not a medication that would make the FDA proud. Less than 1% of its outpatient use is for an FDA indication, and a good portion of the off-label use takes place in psychiatry. These Clinicians who prescribe gabapentinoids off-label for pain should be aware of the limited evidence and should acknowledge to patients that potential benefits are uncertain for most off-label uses. In today’s video, we explore the off-label uses of Gabapentin, also known as Neurontin. While Gabapentin is FDA-approved for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, its off-label uses are more extensive, especially in psychiatry. Gabapentin is a drug that was approved by the FDA in 1993 as an adjunct treatment for epileptic seizures. It has since attained approval for the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children. In addition to its mechanism as an antiepileptic drug, Gabapentin functions as an analgesic, and was approved in 2004 for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Despite its approved uses as an Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant (antiseizure) medication approved by the FDA to treat several conditions. Doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin "off-label" to treat other conditions as well. A 2022 report stated that gabapentin was among the 10 most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve Like gabapentin, it is sometimes used with opiates, with toxic or even lethal results. Similarly, when in combination with alcohol or nervous system depressants, there is the possibility of greater toxicity. Choosing gabapentin and pregabalin: These drugs are widely used off-label as an alternative to benzodiazepines for anxiety disorders. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. With co The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is prescribed to treat numerous symptoms and conditions beyond those for which it's approved by the FDA. Here are some common off-label uses and how the evidence stacks up for each. Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and concomitant CNS-D This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of In December 1993, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted approval for gabapentin, under the brand name Neurontin, for adjunctive therapy of partial seizures. Subsequently, the FDA approved gabapentin in 2000 for treatment of partial seizures in children aged 3 years or older and in 2002 In this nationally representative sample, <1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for approved indications. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |