Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
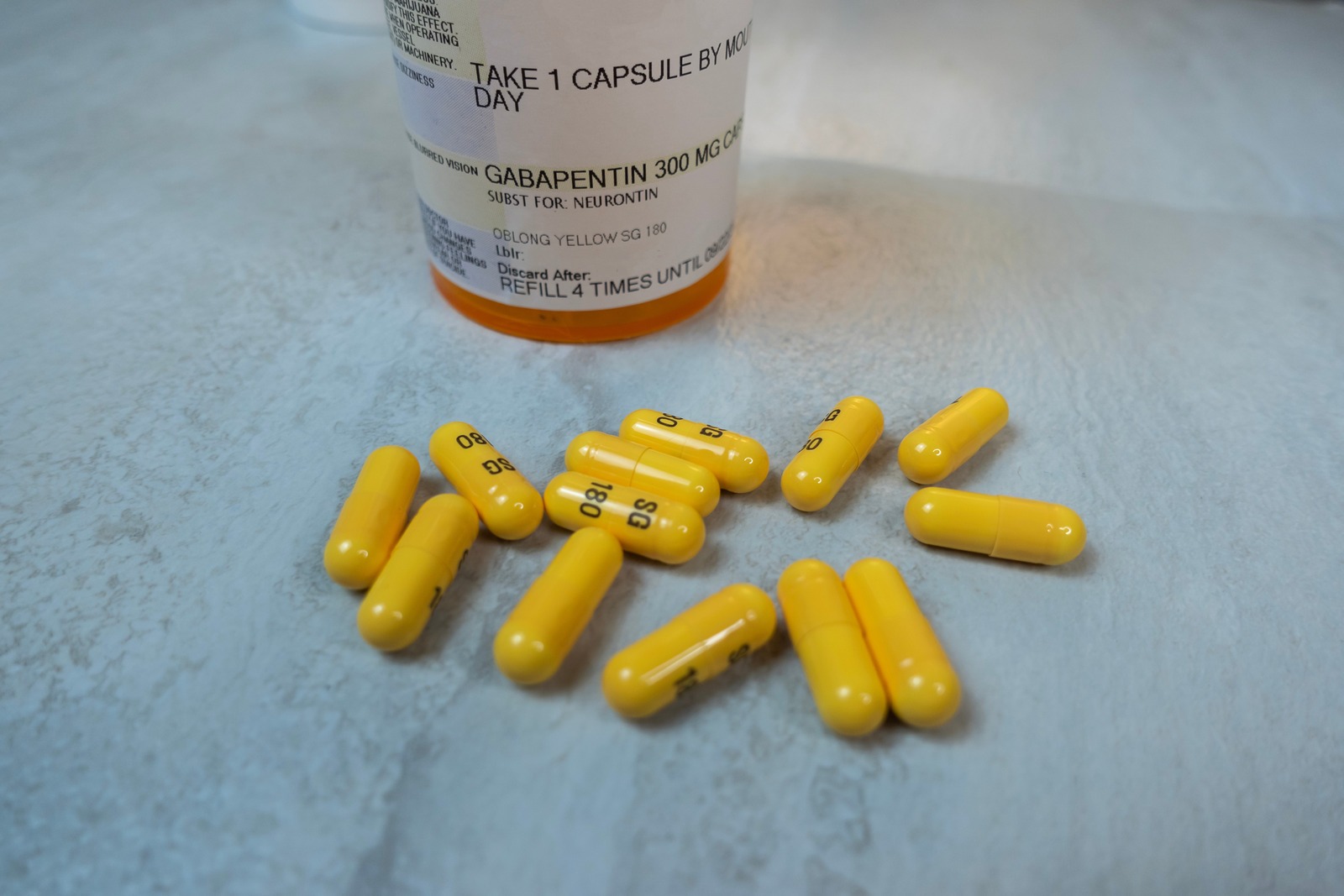 |  |
 | |
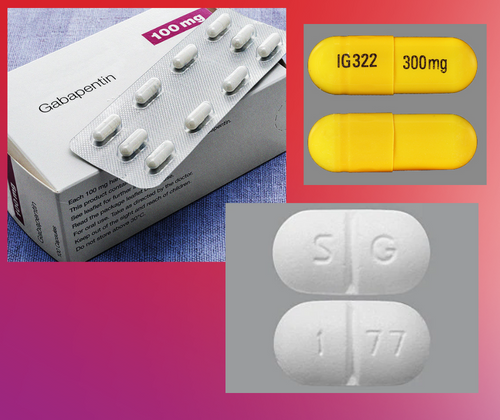
Delirium after gabapentin withdrawal. Case reportCan J Neurol Sci. 2013 Jan;40 (1):126-7. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100017418. Read a letter to the editor on Gabapentin (Neurontin) Abuse, and Delirium Tremens (DTs) upon Withdrawal. Here we present a case of psychotic symptoms associated with a delirium, possibly due to gabapentin withdrawal. Our patient, a 48-year-old female presented to the UMMC emergency department with her family due to a one-week history of altered mental status and generalized muscle aches. Does gabapentin cause withdrawal? Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, when they occur, and what can help. LETTERS TO THE EDITOR Gabapentin Abuse, and Delirium Tremens Upon Gabapentin Withdrawal Sir: Gabapentin is one of a new generation of antiepileptic drugs widely used in recent years for a variety of indications, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, migraine, and bipolar disorder. Delirium After Gabapentin Withdrawal. Case Report Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 September 2014 Finally, benzodiazepines have been used to treat delirium resulting from gabapentin withdrawal (29) and gabapentin has been used to treat withdrawal from both benzodiazepines (80) and alcohol (19, 21). This unusual case of gabapentin dependence and abuse involved toxic delirium, intense cravings, and a prolonged post-withdrawal confusional state reminiscent of ben-zodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin is a central nervous system inhibitory agent with likely gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic and non-GABAergic mechanisms of action. This unusual case of gabapentin dependence and abuse involved toxic delirium, intense cravings, and a prolonged post-withdrawal confusional state reminiscent of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin is a central nervous system inhibitory agent with likely gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic and non-GABAergic mechanisms of action. Abstract In most cases, a sudden interruption of most medications has no major consequences. There are well-recognized therapies that, when withheld, can either lead to the reappearance of the symptoms they were controlling or to signs or symptoms of withdrawal. In this article, we present a table including medications that when interrupted can produce withdrawal syndromes, the signs and Gabapentin abuse, and delirium tremens upon gabapentin withdrawalJ Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Mar;68 (3):483-4. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n0320a. It is especially important to recognize gabapentin withdrawal in critically ill patients because its symptoms overlap with common ICU syndromes such as ICU delirium, severe sepsis, drug reactions, pain, stroke, or serotonin syndrome. Delirium is identified when there is a short-term, persistent disturbance of attention and awareness that differs from baseline and has a tendency to fluctuate. 9–11 The link between gabapentinoids and delirium is controversial, even Leung et al confirm that gabapentin could decrease postoperative delirium in older patients through clinical This case emphasizes the challenges of identifying lesser-known presentations of gabapentin withdrawal, highlights delayed time to resolution following subsequent withdrawal episodes, and stresses the importance of ensuring access to medication and appropriate education to ensure safe transitions of care. 18. Di Fabio R, D’Agostino C, Baldi G, Pierelli F. Delirium after gabapentin withdrawal syndrome in presence of a taper. Can J Neurol Sci. 2013;40 (1):125-126. 19. Mal L, Hart M. Gabapentin withdrawal: case report in an older adult and review of the literature. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61 (9):1635-1637. 20. Like with opiate withdrawal, gabapentin can treat the anxiety and insomnia that can result from alcohol withdrawal. And as an anticonvulsant, it can be helpful in treating withdrawal seizures like delirium tremens. The common signs and symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal syndrome include development of hypertension, tachycardia, agitation, delirium, confusion, anxiety, combativeness, hallucinations, disorientation, paranoid delusions, tremor and increased muscle tone. 11–14 Critical withdrawal symptoms including status epilepticus and catatonia have also Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug for seizures and nerve pain. Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms and how to safely stop taking the medication. Gabapentin has been used to treat neuropathic pain related to visceral hyperalgesia in the neonatal population.5,6 Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog, is thought to inhibit pain via voltage-dependent calcium ion channels in the central nervous system. There is minimal information on the use and side effects of initiating and discontinuing of gabapentin in this population.3,5-7 The OBJECTIVE A protocol was developed for neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) delirium: Step 1, gabapentin for pain or melatonin for sleep; Step 2, add on other Step 1 agent; Step 3, antipsychotics. The purpose of this study was to describe the utility and dosing of gabapentin for NICU delirium. METHODS Retrospective evaluation of NICU patients from January 1, 2021–December 31, 2022 who
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
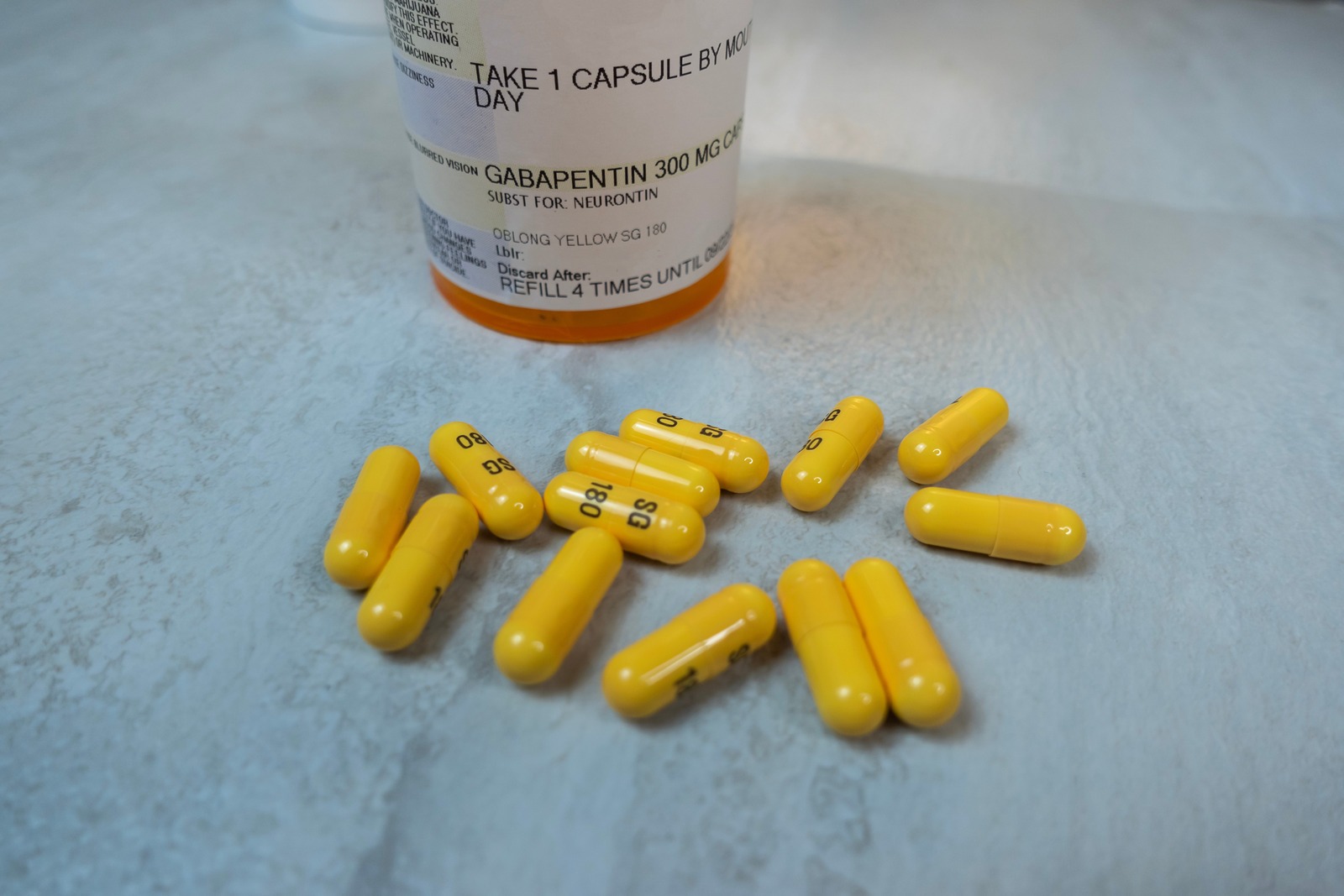 |  |
 | |