Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
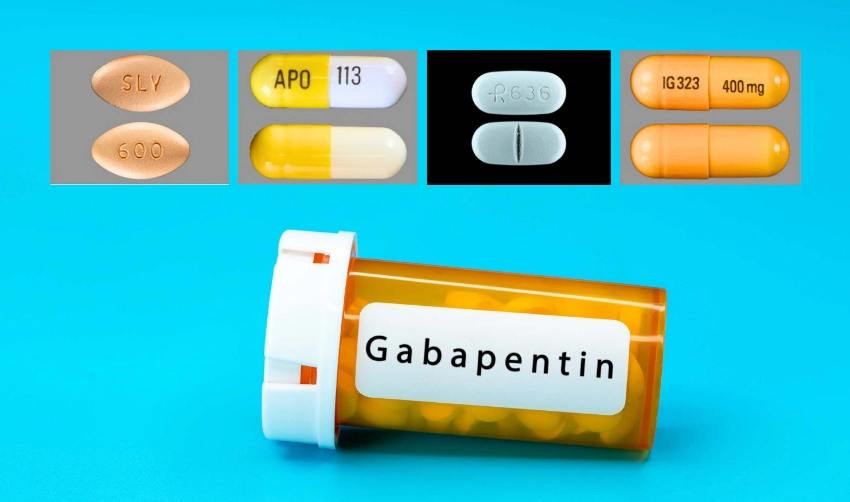 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
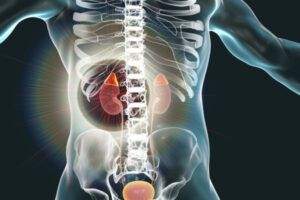
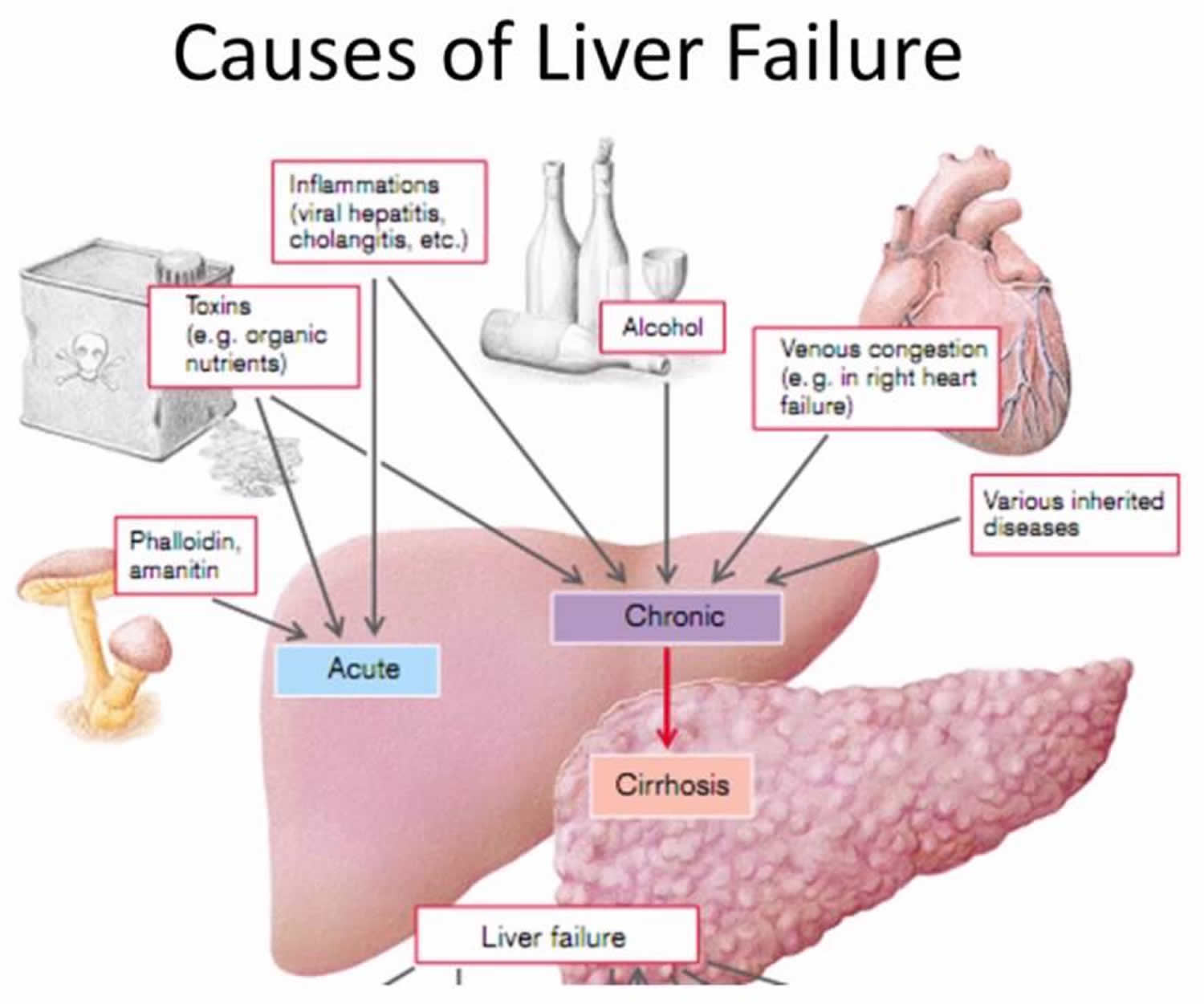
Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. Key takeaways Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. The kidneys, liver, and gastrointestinal tract all play roles in how gabapentin is metabolized and eliminated from the body. Effects on the Kidneys Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Therefore, renal function significantly influences drug levels in the body. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, has infrequently been reported to cause liver injury; however, the causality in the previous reports is contested. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Hi, Gabapentin is exclusively excreted by the Kidneys and undergoes no appreciable metabolism by the Liver. As to whether it is toxic to your Kidneys is probably a question that you should be asking your prescribing doctor. Certainly, fluid retention is listed as a possible side effect and it is also known that Gabapentin toxicity is an issue for people with Kidney disorders. Good luck. Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant drug that’s FDA-approved to treat partial seizures, restless leg syndrome, and nerve pain from shingles, spinal injuries, diabetes, or other conditions. Since the body eliminates gabapentin completely through the kidneys, it’s typically considered safe in patients with pre-existing liver disease. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin is approved by the FDA for treating seizure disorders and neuropathic pain, except for trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is frequently used off-label to treat other pain conditions and psychological disorders, such as anxiety. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). Gabapentin is generally considered safe for the liver, but rare cases of liver damage have been reported. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained popularity for its effectiveness and relatively mild side effects. However, concerns about its impact on liver health have surfaced among patients and healthcare providers. Understanding whether gabapentin Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. People with chronic kidney disease who take gabapentin should be very aware of this as to not cause further damage to their kidneys. I found online somewhere that Gabapentin can inflame the liver, yet, also read that it is not metabolized in the liver at all. I read that incidents of liver problems are less than one percent as stated by Pfizer. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |